Welcome to animals and wildlife in North America!
Mexico, the United States, and Canada might be North America’s most prominent and most noticeable nations. However, this mainland — the third biggest on the planet — is home to 23 sovereign states and 23 non-sovereign domains that stretch as far as possible from Central America up through Greenland.
The sheer extent of the mainland implies that any biological system on Earth can be tracked down in North America — from Greenland’s cold tundras to Costa Rica’s jungles, which you can discover another time by reading about Animals in Costa Rica.
So it is our utmost pleasure to welcome you to the wacky world of animals in North America! Brace yourself for a hilarious hodgepodge of critters, from reindeer to bug monkeys. They may come from opposite ends of the continent, but they’re all part of this gigantic continent. Get ready for deserts, woods, mountains, and everything in between to serve as their playground.
Click below to jump to any section on animals in North America:
Key Points
| Region/Habitat | Notable Animals |
|---|---|
| Mojave Desert | Hares, coyotes |
| Okefenokee Swamp | Crocodiles, beavers |
| Northern Canada | Polar bears, moose |
| Belize Barrier Reef | Manatees, dolphins, humpback whales |
| Rocky Mountains | Bighorn sheep, bobcats, wolverines |
| Woodlands | Raccoons, bobcats, various bird species |
| Coastal Areas | Sea turtles, seals, shorebirds |
| Forests | Black bears, gray wolves, lynx, various bird species |
| Arctic | Arctic foxes, reindeer, musk oxen, snowy owls |
| Wetlands | Alligators, herons, egrets, turtles |
| Marine | Humpback whales, dolphins, sea lions |
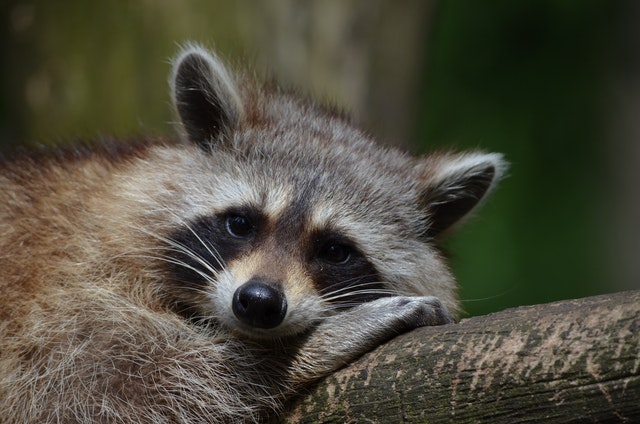
Raccoon

| Scientific Name | Procyon Lotos |
| Lifespan | 2-3 years (in the wild) |
| Conservation Status | Least concern |
| Order | Omnivore |
| Family | Mustelidae |
| Kingdom | Animalia |
Alright, let’s talk about our sneaky little friend, the raccoon. These neighborhood troublemakers measure around 3 feet in length, tail included. And boy, what a tail it is! A whopping 12 inches long, thick, and all ringed up like a fashionable accessory. No wonder they strut around like they own the place.
But here’s the thing: raccoons have a bit of a posture problem. Their back legs are longer than their front legs, so they end up looking like they’ve been partying a bit too hard and can’t quite stand up straight. It’s a perpetual raccoon hangover waddle.
Now, let’s talk about those hands… err, I mean front feet. These critters have five incredibly skilled toes, which they use to play the ultimate game of “make heads or tails” of whatever food they can find. They’re like the culinary masters of the animal kingdom, with a knack for turning trash into gourmet meals.
Speaking of meals, raccoons come in all shapes and sizes. Adult raccoons can weigh anywhere between 15 to 40 pounds, depending on their genetic makeup, age, available food, and living space. Some hefty fellas have even tipped the scales at over 60 pounds! But here’s a fun fact: wild raccoons are usually a bit lighter than their urban counterparts. Those city slickers have figured out how to live the good life, surviving on handouts, pet food, and the delightful treasures found in garbage cans.
While raccoons have a preference for the great outdoors, particularly near streams or water sources, they’ve proven to be quite adaptable creatures. They’ve made themselves at home in various situations, even here in Washington. This has caused some hilarious situations such as the Raccoon’s Dunkin’ Donuts Drive-Thru that went viral. So next time you spot a raccoon doing its wobbly walk or indulging in a culinary adventure in your trash can, just remember they’re the true masters of mischief, always up for an urban escapade or a gourmet dumpster feast.
Let’s talk about the raccoon party in the big city! These clever critters know how to live it up, thanks to limited hunting and plenty of human-provided goodies.We’ve even seen a Raccoon Scaling a Skyscraper! With their insatiable appetites, they’ll chow down on just about anything, especially if it comes from the water. Shellfish, crayfish, frogs, fish, and snails? Yup, raccoons are all over that menu. But don’t be fooled, they’re not picky eaters. Bugs, slugs, dead animals, fruits, veggies, nuts, seeds – you name it, they’ll munch on it!
When it comes to hanging out with humans, raccoons aren’t shy about raiding our trash cans and snacking on pet food. While they might not be the most skilled hunters, they can still nab a few young gophers, squirrels, mice, and rodents here and there. Except during the breeding season, raccoons prefer to fly solo. But when there’s a feast to be had, they’ll gather ’round and share the food bonanza.
These crafty critters are true omnivores, devouring anything within their reach. They’ve got a taste for shellfish, insects, mollusks, and even the occasional yellow creature. Oh, and let’s not forget their love for crab and other easy-to-catch prey. Sorry birds and mammals, you’re just not as convenient!
In urban areas, raccoons are pros at dumpster diving, always on the lookout for tasty treats. When it comes to matters of the heart, raccoons have a specific mating season from January to June, with the peak happening in March and April. After a cozy 65-day gestation period, adorable raccoon packs are born.
These little rascals hang out in their cozy den until they’re about seven weeks old. Once they can walk, run, climb, and explore alternate hideouts, they venture out with their momma. At around eight to ten weeks old, these youngsters start foraging for themselves, ready to take on the world, one snack at a time!
Where to find Racoons
If you’re on the lookout for raccoons in North America, you’re in luck! These mischievous creatures can be found in a wide range of habitats across the continent. From the lush forests of Canada and the United States to the vibrant urban landscapes, raccoons have managed to carve out a niche for themselves.
In more natural environments, such as woodlands and wetlands, raccoons thrive in areas with access to water sources. They are often seen near rivers, lakes, and marshes, as they have a fondness for hunting and foraging around these areas.
But raccoons have also adapted surprisingly well to urban environments. You’ll find them scampering through city streets, rummaging through trash cans, and even nesting in attics and crawl spaces. They’ve become quite the urban dwellers, making their homes in parks, residential neighborhoods, and anywhere they can find a steady food supply.
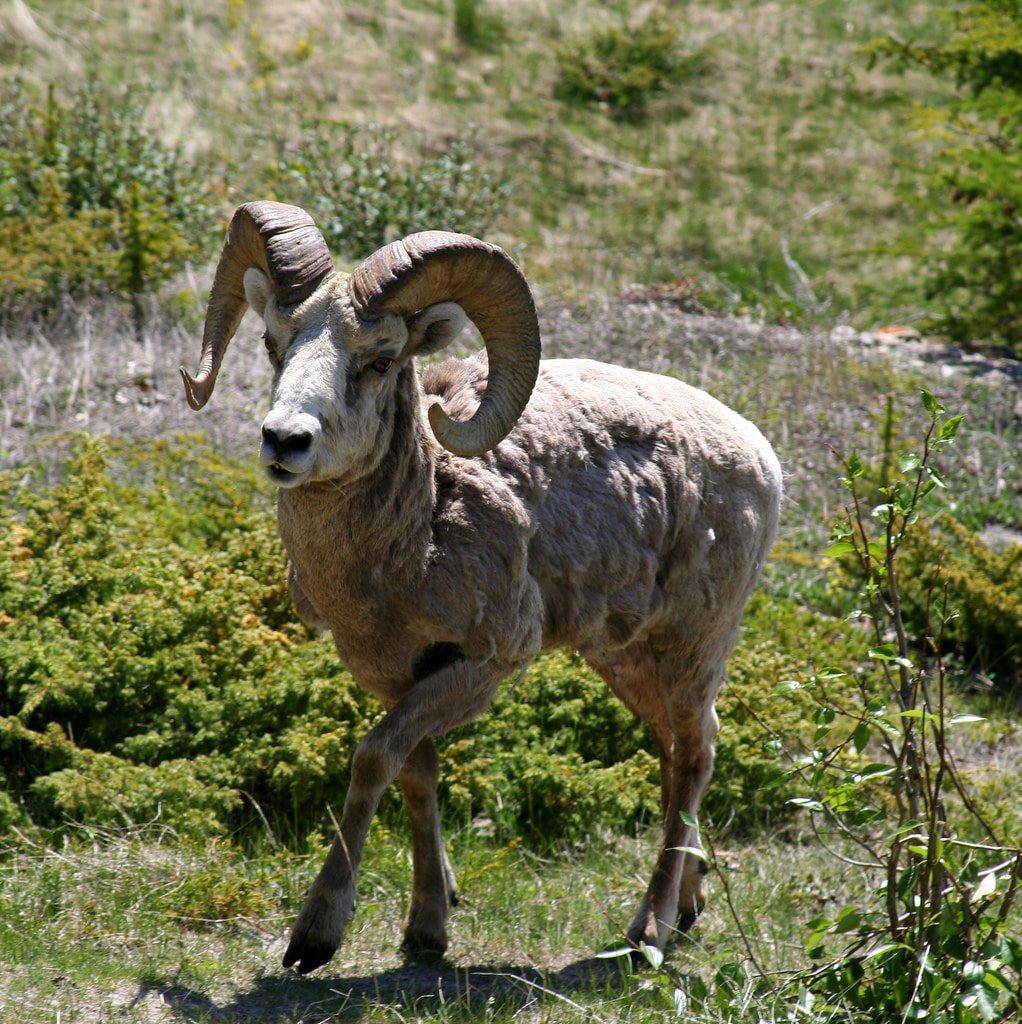
Bighorn Sheep

| Scientific Name | Ovis canadensis |
| Weight | 70 kg |
| Conservation status | Least concern |
| Order | Herbivorous |
| Family | Boviidae |
Get ready to meet the true tough guys of the animal kingdom! We’re talking about the bighorn sheep, sporting bulging muscles, massive horns, and a glorious coat of chocolate brown fur. These fellas tip the scales at a solid 73-113 kg, making them a bit heftier than your average sheep. Ladies weigh in at a respectable 159 kg and stand about 40 inches tall at the shoulder.
With their eyes strategically placed on the front of their heads, these sheep have eyesight that could put a hawk to shame. They’ve got keen hearing and an impressive sense of smell, which comes in handy when searching for food or avoiding pesky predators. Now, hold on to your hats because we’ve got not one, but two species of wild sheep in the house!
First up, we’ve got the bighorn sheep, strutting its stuff in the North Dakota region with a magnificent set of horns that would make any Viking jealous. And let’s not forget about the Dall sheep, another wild woolly wonder. Some smarty-pants researchers claim that the bighorn sheep is just one species out of the four subspecies of wild sheep, including the Rocky Mountain, Sierra Nevada, and California bighorn sheep. Talk about a diverse family!
Now, let’s talk about those horns. The boys, or rams, rock some seriously curved and weighty headgear, tipping the scales at a hefty 14 kg. As these guys age, their horns grow bigger and badder, reaching a whopping 0.9 meters in length with a base circumference of around 0.3 meters. The ladies, or ewes, have shorter horns but still know how to use them like champs when it comes to chowing down on grub or duking it out with other critters.
Sure, they may not be the most nimble creatures out there, but when it comes to climbing, they’re unbeatable. Predators ain’t got nothing on these agile mountaineers! Come summertime, you’ll find them feasting on clover, sedges, and grasses, while in winter, they munch on woody plants like sage and willow. Oh, and did we mention they even snack on cacti when they find themselves in the desert? These sheep are real culinary daredevils!
So, there you have it, the bighorn and Dall sheep, the cool cats of the wild sheep world. They’ve got the muscles, the horns, and the taste buds of champions. Give ’em a round of applause, folks!
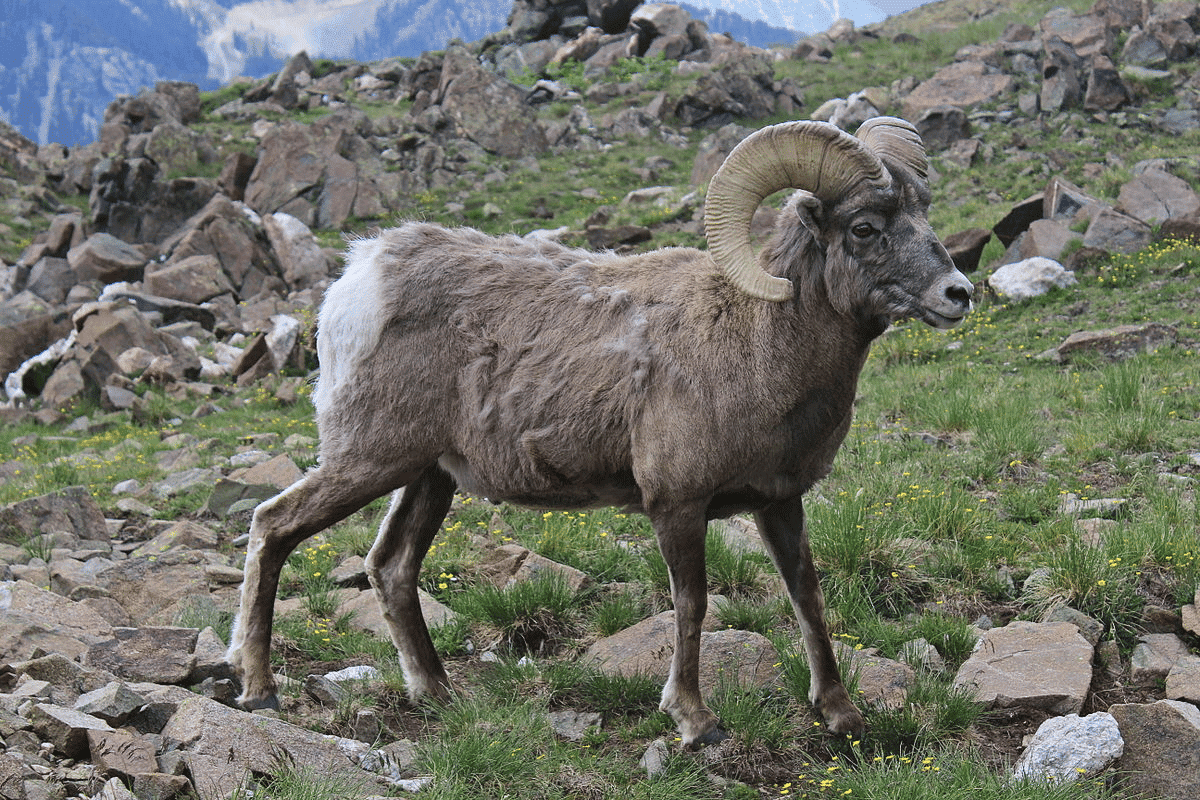
Where to find Big Horn Sheep
If you’re on the lookout for the majestic bighorn sheep in North America, you’re in for a wild adventure! These rugged creatures can be found in various locations across the continent, showcasing their impressive horns and daring nature.
One popular spot to catch a glimpse of bighorn sheep is in the North Dakota region. There, you’ll witness these magnificent beasts roaming the vast landscapes, showing off their magnificent headgear.
But that’s not all! The bighorn sheep can also be spotted in other regions of North America. Keep your eyes peeled while exploring the Rocky Mountains, where these agile climbers make their homes. The Sierra Nevada mountain range is another prime location to search for these sure-footed creatures, gracefully navigating the rocky terrain.
If you find yourself in California, be on the lookout for the California bighorn sheep, a subspecies of these incredible animals. They can be found in specific areas, so check with local wildlife authorities for the best spots to catch a glimpse.
Bobcat
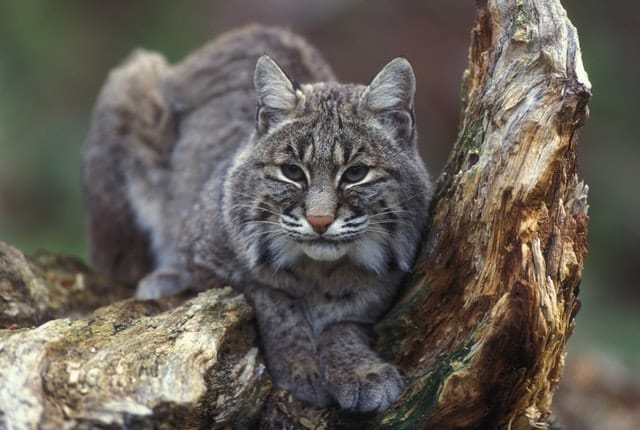

| Scientific Name | Lynx Rufus |
| Weight | 6-18 kg |
| Conservation status | Least concern |
| Order | Carnivora |
| Family | Felidae |
Meet the wildcat, the ultimate mix of funny features! Picture a long-legged feline with humongous paws, a hilariously short body, and tufted ears. This cat measures around 60-100 cm (excluding its 10-20-cm tail), stands 50-60 cm tall at the shoulder, and weighs 7-15 kg. Its fur, not as fancy as the lynx’s, comes in shades of pale brown to blushing, adorned with dull spots.
But that’s not all! The bobcat hasa white underbelly and a tail tip that’s dark on top and white underneath. During the day, these cats love to lounge in cozy spots like vacant trees or secluded rocks, each cat claiming different dens in its home range. They’re super territorial and mark their turf with scents and scratch marks on trees. Talk about leaving their unique calling card!
Now, here’s the funny part: while the parents’ massive territory might overlap with a few other females, they won’t team up until it’s time for some winter romance. The rest of the year, these catamounts prefer to steer clear of each other, reducing the chances of getting hurt in a brawl. Smart move, right?
Believe it or not, the wildcat is not much of a talker, except during the mating season when it can’t help but yowl and mumble its heart out. You might spot this elusive creature in rural areas, as it’s a nighttime loner that feels equally at home in both woods and deserts. They’re not big on tree-climbing or swimming like their lynx cousins, but boy, can they chow down on rodents, rabbits, hares, and birds!
When it comes to romance, spring is the time for love (sometimes with a repeat performance later in the year). After a gestation period of about 50 days, a litter of one to six adorable kittens is born. They’re definitely the cutest little troublemakers in town!
Let’s not forget the wildcat’s economic significance too. They’re quite the catch as furbearers and play a vital role in keeping rodent and rabbit populations in check. Talk about a cat with a job!
So, there you have it—the wildcat, a night owl with a quirky personality and a crucial role to play in the animal kingdom. Check out the link for some visual hilarity!
Where to find Bobcats
Ah, the elusive and mischievous bobcats of North America! If you’re looking to spot these cunning creatures, you’ll need to know where to search. They’re known to roam across a wide range of habitats, so keep your eyes peeled in the following areas:
- Woodlands and Forests: Bobcats feel right at home in dense woodlands and forests. Look for them hiding among the trees, stalking their prey with their stealthy moves.
- Mountains and Hills: These agile climbers love to explore the rocky terrain of mountains and hills. Keep an eye out for bobcats gracefully maneuvering their way through the rugged landscape.
- Deserts and Arid Regions: Believe it or not, bobcats can adapt to the arid environments of deserts. Scan the sandy dunes and rocky outcrops for these adaptable felines.
- Coastal Areas: Bobcats are no strangers to the coastal regions of North America. In some areas, they’ve learned to navigate the coastal marshes and dunes, showing off their versatile nature.
- Urban Fringes: Don’t be surprised if you encounter a bobcat on the outskirts of urban areas. These resourceful felines have been known to explore suburban neighborhoods in search of food and shelter.
Wolverine
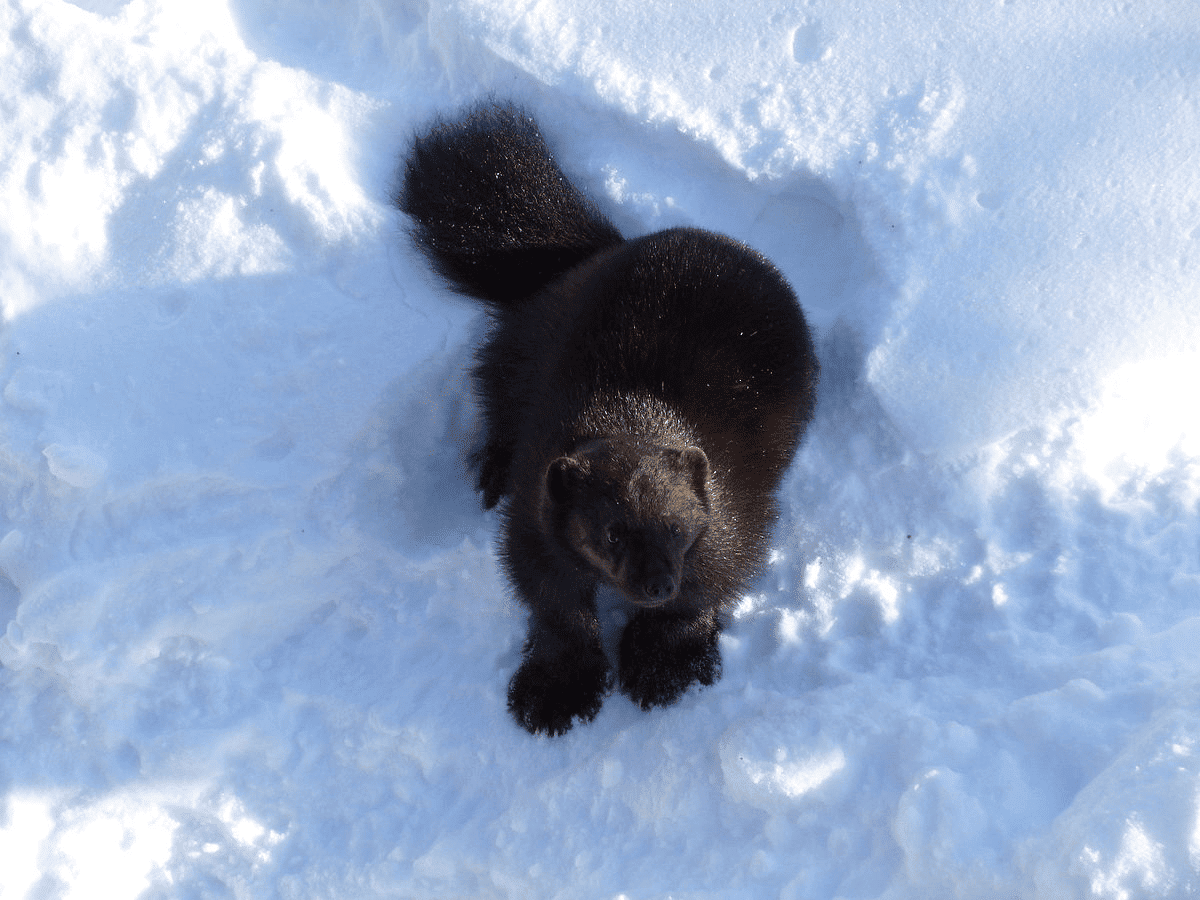

| Scientific Name | Gulo Gulo |
| Weight | 9-25kg |
| Conservation Status | Least concern |
| Order | Carnivora |
| Family | Mustelidae |
| Kingdom | Animalia |
Meet the Wolverine, the fearless and ferocious troublemaker of the animal kingdom! Don’t believe us? Read naother one fo our articles about a Wolverine Taking On A Bear. With its cunning, boldness, and insatiable appetite, this furry beast knows no bounds. It’s not afraid to raid traplines, gobble up food stocks, or snatch anything compact it can get its paws on. Oh, and let’s not forget its distinct odor that can clear out an entire club!
When the night falls, the Wolverine becomes the ultimate predator, chasing down any game it fancies. Sheep, deer, wolves, and even little bears are all fair game for this audacious creature. And when it comes to dining options, Wolverines are versatile scavengers. They have no qualms about feasting on the carcasses of elk, caribou, and other unfortunate animals. Talk about having a taste for the macabre!
Here’s the kicker: no creature, except humans, dares to challenge the Wolverine. Its luxurious fur is highly prized for parkas because it effortlessly brushes off ice and frozen breath. Talk about fashion and function! While the Wolverine prefers to keep to itself for most of the year, it indulges in a short romantic fling in February or March. And guess what? A litter of one to five rambunctious offspring is the result. Brace yourselves, world!
In the summer, Wolverines try to balance their diet with a touch of vegan goodness. Plants and berries make a brief appearance on their menu. But let’s be honest, meat is their true love. They’re nimble hunters, taking down rabbits and rodents with ease. But here’s the twist: they’re not afraid to take on larger prey like caribou if they sense weakness or injury. Talk about overconfidence!
These audacious eaters aren’t picky when it comes to their meals. They’ll happily feast on the bodies of larger animals like elk, deer, and caribou. It’s survival of the hungriest! Oh, and did we mention that Wolverines are scent-marking masters? Males proudly mark their territories, and if you come across their aromatic calling card, it’s best to steer clear!
But here’s a surprise: Wolverines are social butterflies, at least when it comes to romance. They share their domains with multiple females and are believed to be quite the polygamists. When it’s time to bring new Wolverines into the world, the females nestle in the snow or cozy up under some cover, giving birth to a litter of adorable fluffballs every spring or late winter. It’s like a fluffy family reunion!
Wolverines have this fabulous, heavy fur that used to make them prime targets for hunters in North America. Their luxurious locks were in high demand for lining parkas. But don’t worry, these days they’re much more protected, and their fashion choices are no longer a threat. In the summer, Wolverines might nibble on a few plants and berries, but let’s be real—they’re meat enthusiasts through and through. From rabbits to caribou, they’re always up for a carnivorous adventure!
Where to find Wolverines
- Alaska: Head north to the vast wilderness of Alaska, where Wolverines roam free. The rugged landscapes and abundant prey make it an ideal habitat for these furry daredevils.
- Rocky Mountains: Strap on your hiking boots and venture into the Rocky Mountains. These majestic peaks provide a perfect playground for Wolverines, who love to explore the high-altitude terrain.
- Yukon and Northwest Territories: If you’re up for a true northern expedition, set your sights on the Yukon and Northwest Territories in Canada. These remote, snow-covered regions offer prime real estate for Wolverines to thrive.
- Cascades and Sierra Nevada: Journey to the western United States and explore the Cascade and Sierra Nevada mountain ranges. These rugged areas provide the Wolverines with ample opportunities for hunting and mischief.
- Northern Canada: Don’t forget to explore the vast wilderness of northern Canada, where Wolverines can be found in abundance. From Labrador to Nunavut, these remote regions are a haven for these crafty critters.
Summary of Animals and Wildlife in North America
Along with the variety of critters, you’d expect to discover; this area is home to deserts, woods, mountains, and places in between.
Hares and coyotes live in the Mojave Desert, crocodiles and beavers own the Okefenokee Swamp, while polar bears and moose are particularly interested in the northernmost region of Canada. In North America, more than 100 distinct ecoregions have been identified, leading to a remarkably diverse dispersion of both human civilization and animal species.
However, the proximity of North America to the Pacific and Atlantic suggests that the marine form is also prevalent. Manatees and dolphins make up only a tiny percentage of the native untamed life in the Belize Barrier Reef, in contrast to the enormous humpback whales that roam the North Atlantic.
If you enjoyed reading about the animals in North America, check out the top 10 most endangered animals in 2022 and the five rare species next! Also check out Wildlife in California, or Wildlife in Colorado.
Ah, America is a diverse continent with a wide range of remarkable animals. While it’s difficult to pinpoint a single “main” animal, some iconic species often associated with America include the bald eagle, bison, and the American black bear.
No, lions are not native to North America. They are typically found in Africa, particularly in savannah and grassland habitats.
One of the rarest North American animals is the red wolf. Once ranging throughout the southeastern United States, the red wolf is now critically endangered and confined to a limited number of protected areas.
While bears are certainly prevalent in North America, particularly species like the American black bear, grizzly bear, and polar bear, they are not exclusive to this continent. Bears can also be found in other parts of the world, such as Europe and Asia.
African lions have different ecological requirements and adaptations than the native North American wildlife. Introducing African lions into the American ecosystem would pose significant challenges and disrupt the balance of native species. Therefore, it is not feasible or advisable to introduce African lions to America.
Tigers are not native to America. However, there are certain captive populations of tigers in zoos, sanctuaries, and private facilities across the country. These tigers are descendants of captive-bred individuals and are not part of the native American wildlife.
- Animals and Wildlife in Colorado - April 24, 2024
- Best Places to see Sloths - April 24, 2024
- Where to See Alligators in the Wild - April 24, 2024





