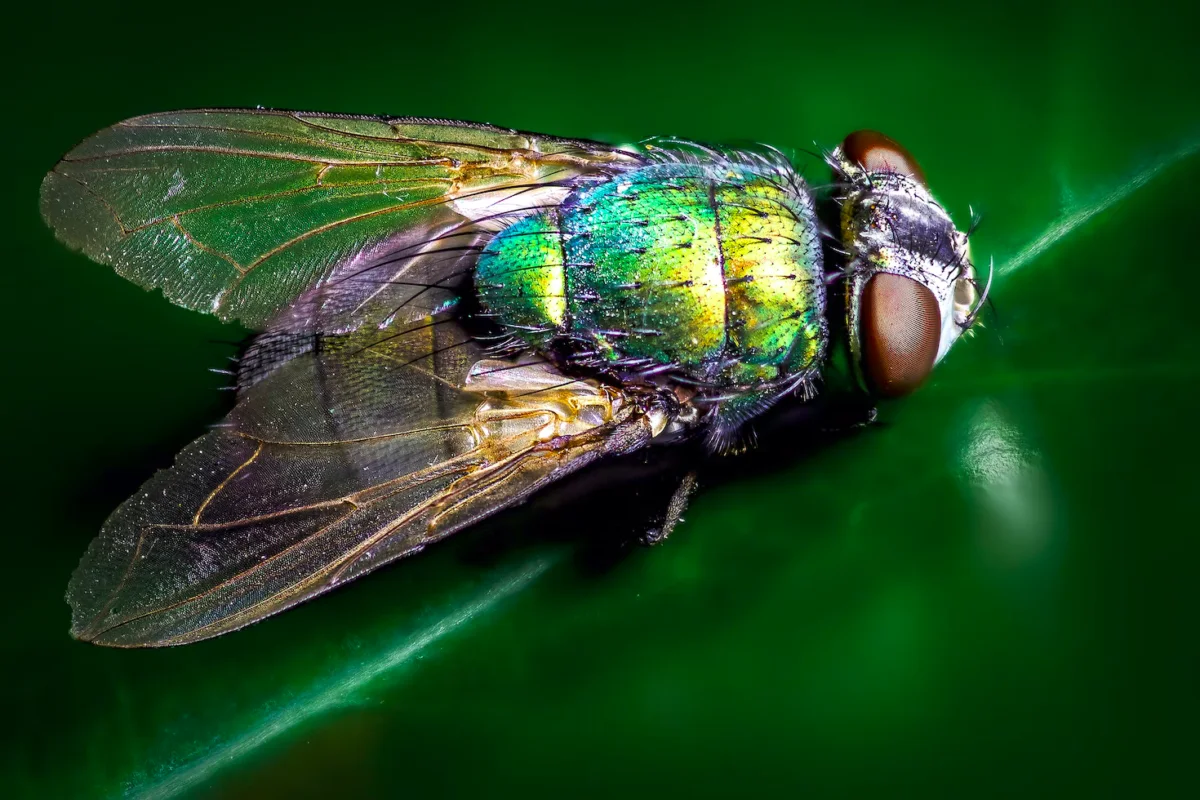
Ever wondered how long a fly lives? Well, you’ve landed in the right place to discover all the answers!

Flies, also known as Diptera, are small, winged insects known for their quick movements and ability to spread disease. While they are often seen as pests, they play an essential role in the ecosystem, serving as pollinators and food sources for other animals.
Flies have a relatively short lifespan, with most species living for just a few days to several weeks. However, the exact lifespan of a fly can vary based on several factors, including its species, the environment in which it lives, and access to food and water.
Let’s take a closer look at the characteristics that determine the lifespan of a fly and provide an overview of how long these insects typically live.
Are you interested in The 10 Longest Living Animals?
Want to jump ahead? Click below
Appearance Of A Fly
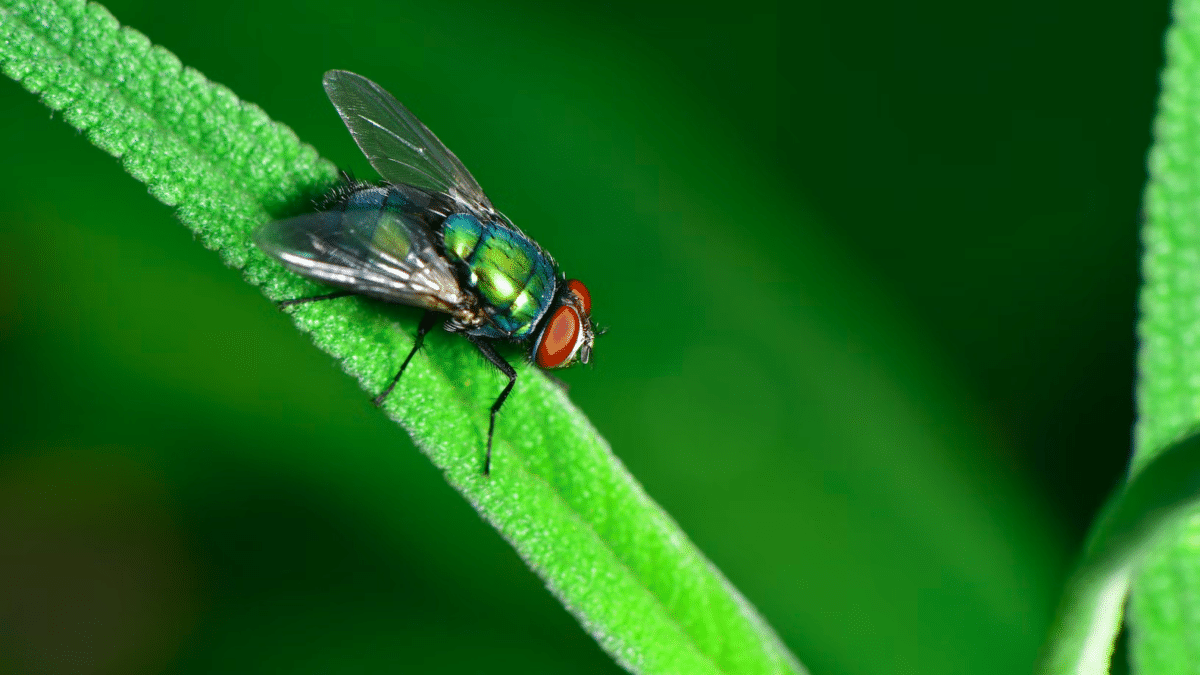

Flies is an insect characterized by its small size, two wings, and six legs. Their bodies are generally oval-shaped and flattened from top to bottom, with a shiny appearance. They are typically between 6 to 12 millimeters long and come in various colors, including black, gray, and green.
At the front of their bodies, flies have a pair of large compound eyes, which are made up of many individual lenses that allow them to see in multiple directions simultaneously. These eyes are often brightly colored and can give the fly a distinctive appearance. Flies also have a pair of small antennae on their heads, which are used for detecting scents and other sensory information.
The wings of a fly are typically transparent or translucent and have a veined appearance. They are used for flight and can beat at breakneck speeds, allowing flies to hover in place and change direction quickly. Flies have a set of halteres, small knob-like structures that act as stabilizers during flight and help maintain the fly’s balance.
The legs of a fly are thin and often covered in tiny hairs, which help them to cling to surfaces such as walls and ceilings. At the end of each leg, flies have a pair of claws used for gripping onto surfaces and climbing. They also have small pads on their feet that secrete a sticky substance, allowing them to walk on smooth surfaces.
Although flies are typically associated with disgust and annoyance due to their association with unclean environments and disease transmission, their physical characteristics are unique and intricate, making them a fascinating subject of study for scientists and entomologists.
Understanding The Life Span Of Flies
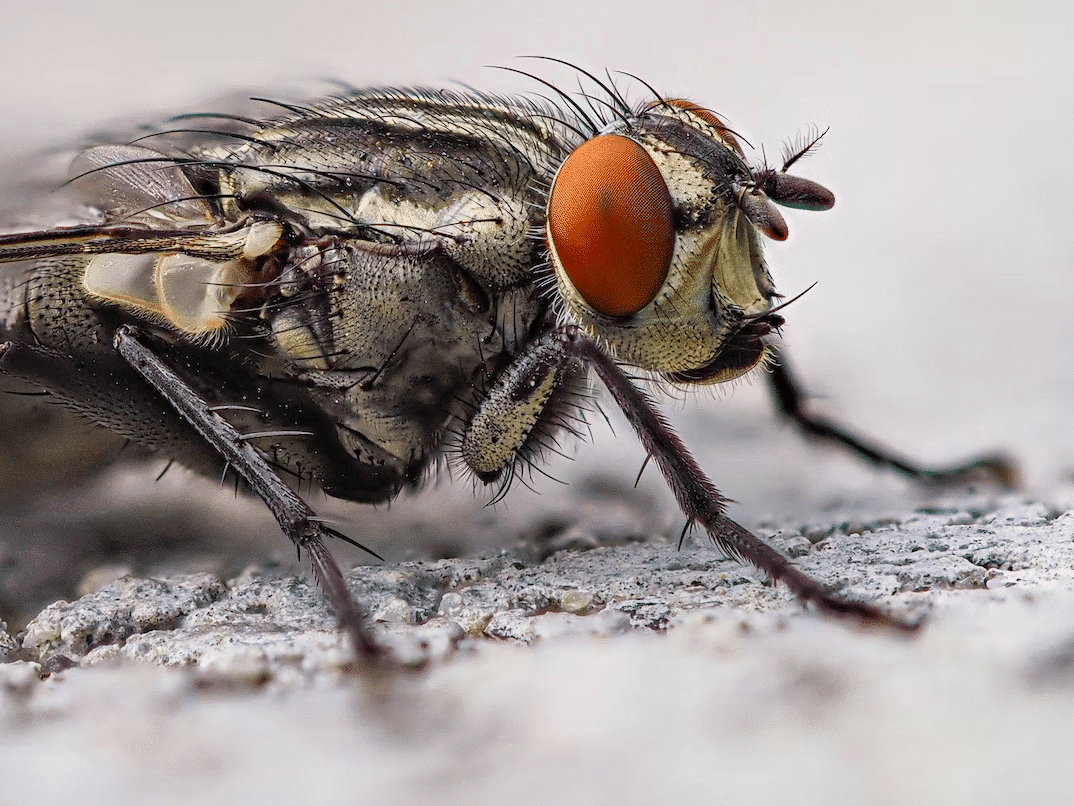
Flies are common insects in almost every corner of the world. While these insects play an essential role in the ecosystem, they are also considered pests worldwide. Understanding the lifespan of flies is crucial for controlling their populations and preventing the spread of diseases.
The lifespan of flies is affected by several factors, including the species of fly, environmental conditions, availability of food, and predation. On average, house flies live for about 15 to 25 days, while fruit flies live for about 30 days.
Learn about the 8 Foods, Fruits, & Scents Fruit Flies Are Attracted To.
Depending on their needs and environment, different flies may live longer or shorter periods.
Good nutrition and ideal environmental conditions can extend the lifespan of flies. On the other hand, poor nutrition and unfavorable environmental conditions can shorten the lifespan of flies. The presence of predators can also significantly reduce the lifespan of these insects.
Understanding the lifespan of flies is essential for controlling their populations and preventing the spread of diseases. By considering the factors that affect their lifespan, we can better understand how to manage fly populations sustainably and effectively. Whether you are a farmer, a pest control professional, or just a curious individual, it is good to have basic information about the lifespan of flies and the factors that influence it.
Importance Of Studying The Lifespan Of Flies
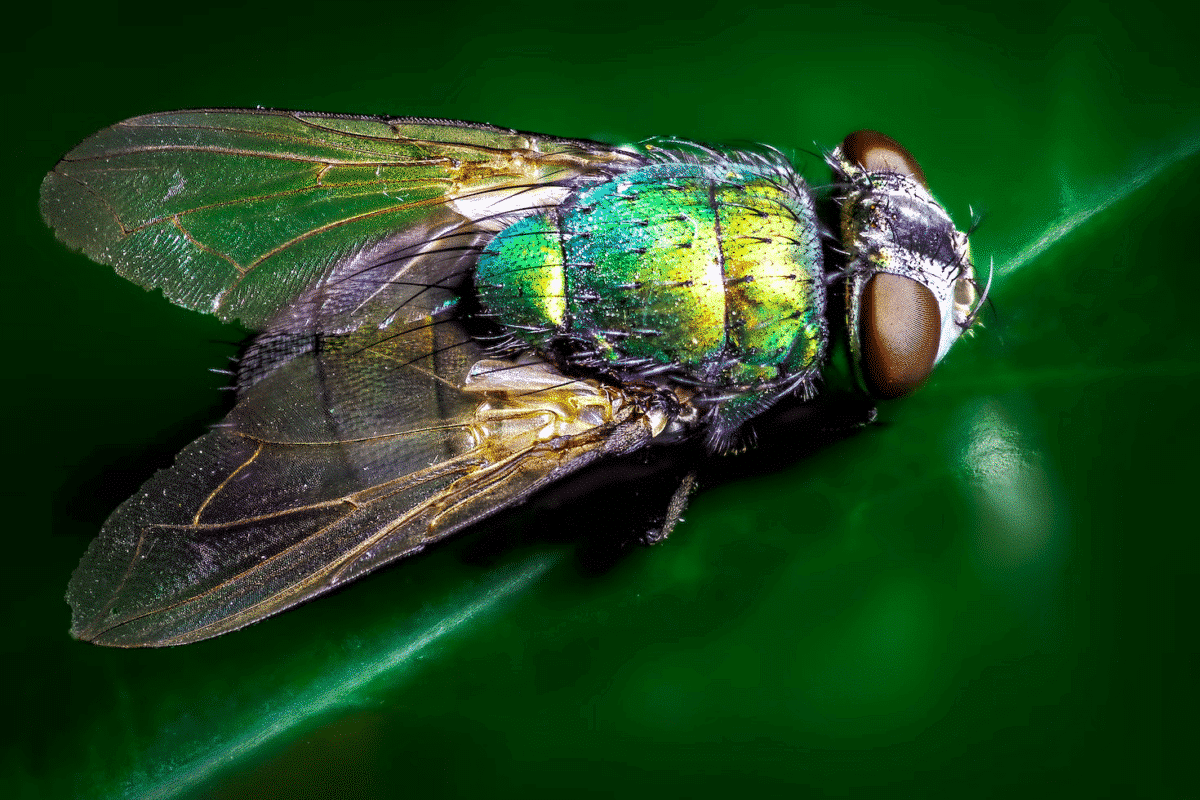
Studying the lifespan of flies holds significant importance due to their abundance and wide distribution across the world. These insects are crucial components of the ecosystem, serving as pollinators, decomposers, and a source of food for various animals.
To effectively manage fly populations and prevent the spread of diseases, it is essential to understand the lifespan of these insects.
Studying the lifespan of flies can provide valuable information about their behavior, reproductive capabilities, and environmental requirements. This information is vital in developing effective strategies for controlling fly populations and reducing the spread of diseases.
For example, understanding the average lifespan of flies can help determine the frequency of treatments needed to manage their people. In turn, this can help reduce the use of insecticides, adversely affecting the environment and human health.
In addition, studying the lifespan of flies can also help understand the impact of environmental factors on their populations. Changes in temperature, humidity, and food availability can significantly affect flies’ lifespan.
When we study these things, we can learn what helps or stops flies from growing in number. This information helps us create plans to control fly populations that are good for the environment.
Different Fly Species
Flies are found throughout the world. Many people often wonder how long these pests can live despite their abundance.
House Flies
House flies are found in homes and other buildings. They are known for their dirty habits, as they feed on rotting organic matter and can carry various diseases. House flies have a relatively short lifespan, typically 15 to 25 days. This short lifespan is due to temperature, humidity, access to food, and susceptibility to predators and parasites.
Fruit Flies
Fruit flies, or vinegar flies, are common in homes and are often found near fruit or other sweet, sugary substances. These flies are generally smaller than house flies and have a slightly longer lifespan, typically living for several weeks. The lifespan of a fruit fly can be influenced by the same environmental factors as house flies, as well as the availability of their preferred food source.
Soldier Flies
Soldier flies are giant, robust insects commonly found near water sources. These flies have a longer lifespan than house flies or fruit flies, typically for several months. Factors like temperature, humidity, and food availability influence the lifespan of a soldier fly.
Mayflies
Mayflies are an aquatic species of fly that are found near freshwater sources. These flies have a very short lifespan, typically just a few days.
Life Cycle Of A Fly
The life cycle of a fly is a fascinating process, including several stages from egg to adult. Understanding the life cycle of a fly is essential for controlling its population and preventing the spread of diseases.
Egg Stage: Fly life begins with an egg. Female flies lay their eggs in damp and decaying material, such as leftover food or animal waste. The eggs usually hatch within 24 hours.
Larval Stage: After hatching, the larvae emerge and feed on the surrounding organic material. This stage is also known as the maggot stage, and they feed voraciously, proliferating and molting several times.
Pupae Stage: After several days of feeding, the larvae will burrow into the organic material to pupate. During this stage, the larvae transform into the pupae stage, the transitional stage between the larval and adult stages.
Adult Stage: After a few days of pupation, the fly emerges from its casing as an adult. An adult fly has a thin body, two wings, and two compound eyes. It can fly and eat as soon as it comes out. Female flies can start laying eggs a few days after they become adults.
The LifeSpan Of A Fly

There are numerous internal and external factors, including
- Species: Different species of flies have different life spans. For example, the house fly has a lifespan of about 15 to 30 days, while the fruit fly can live up to 60 days.
- Environment: The environment in which a fly lives can significantly impact its life span. For example, temperature, humidity, and the availability of food and water can all play a role in determining a fly’s life span. A warm and humid environment can shorten the lifespan of a fly, while a cooler, drier climate can extend it.
- Diet: A fly with access to a high-quality diet rich in nutrients and energy typically has a longer lifespan than one poorly fed.
- Genetics: The genetics of a fly also play a pivotal role in its lifespan.
- Parasites and diseases: Flies can be infected with various parasites and diseases that can shorten their lifespan. For example, some parasitic mites can cause significant harm to flies, reducing their life span by several days.
- Predation: It is another factor that can impact the lifespan of a fly. Flies are a common food source for many predators, including spiders, birds, and lizards. The predation risk can cause a fly to shorten its lifespan, as it will try to reproduce as quickly as possible.
- Stress: Exposure to high levels of stress hormones can cause a fly to have a shorter life span than one that experiences low levels of stress.
The Average Lifespan Of Flies
Generally, the lifespan of a common housefly is typically around 30 days. Other flies, such as the fruit fly or vinegar fly, have an average lifespan of about 40-50 days.
In ideal conditions, some flies can live up to several months. It’s important to note that their lifespan is heavily influenced by temperature, food and water access, and predators’ presence.
The lifespan of different species of flies can vary greatly. Some types of flies and their average lifespans include
Here are the lifespans of three different types of flies:
- House fly: 15-25 days
- Fruit fly: 30-40 days
- Blowfly: 8-10 days
Factors Lessning Lifespan Of Flies
Flies have a limited lifespan considering several factors can shorten the lifespan of flies and contribute to their early death. These factors include:
- Environmental Conditions
Flies are highly susceptible to temperature, humidity, and air quality changes. Extreme heat, cold, or dryness can cause dehydration and stress to the fly, which can shorten its lifespan.
- Disease
It can include infections caused by bacteria, viruses, and parasites, which can shorten the lifespan of flies.
- Parasitism
Flies can be targeted by parasites such as mites, lice, and wasps, which feed on their blood and other bodily fluids. It can cause significant damage to the fly and ultimately lead to its death.
- Predation
Flies are preyed upon by many other species, including birds, spiders, and reptiles. These predators quickly reduce the population of flies and limit their lifespan.
- Nutritional Deficiency
Flies require a balanced diet to thrive, and deficiencies in essential nutrients such as carbohydrates, proteins, and vitamins can impact their overall health and lifespan.
- Aging
Like all living creatures, flies undergo aging, characterized by a decline in physical and physiological functions.
Impact Of Human Activities On Fly Lifespan

Pesticide
Pesticides are widely used to control insect populations but can harm other species, including flies. Pesticides can affect the lifespan of flies in two ways: direct toxicity and indirect toxicity. Direct toxicity occurs when flies are exposed to the chemical and die shortly after. Indirect toxicity occurs when the chemical affects the insects’ food source, causing a decline in their population over time.
Flies feed on various plants, including crops, and their food sources can be contaminated with pesticides. The chemical exposure reduces the lifespan of flies, which in turn can disrupt the food chain and have a ripple effect on other species. Additionally, the decline in the fly population can increase other pests, leading to the need for even more pesticides and further exacerbating the problem.
Climate Change
Climate change is another human activity that affects fly lifespan. Flies are susceptible to changes in temperature, and even slight changes can significantly impact their survival. As temperatures rise, fly metabolism increases, causing them to consume more food and deplete their energy reserves more quickly. It shortens their lifespan and reduces their ability to reproduce.
Droughts can reduce food availability, while floods can destroy breeding grounds, leading to a decline in the fly population. These events can significantly impact flies’ longevity, reducing their lifespan and disrupting the ecosystem.
Habitat Destruction
Habitat destruction is another human activity that affects fly populations. As humans continue to develop and urbanize, natural habitats are being destroyed, causing the loss of food and breeding grounds for many species, including flies. The reduced available habitat can result in a decline in the fly population, which can ripple effect on other species that rely on flies for food.
Moreover, habitat destruction can also increase the exposure of flies to environmental stressors, such as pollutants and chemicals, which can further shorten their lifespan. In addition, the loss of habitats can result in the fragmentation of fly populations, making it more difficult for them to find mates and reproduce, leading to a decline in their population over time.
Pollution
Pollution is another human activity that can impact the lifespan of flies. Polluted environments can contain toxic substances, such as heavy metals and chemicals, affecting flies’ health and reducing their lifespan. Pollution can also reduce the availability of food and breeding grounds, further exacerbating the problem.
Flies play a vital role in many ecosystems, and human activities can significantly impact their populations. By understanding the impact of human actions on fly lifespan, we can take steps to mitigate these effects and protect these important insects.
Wrapping up on Understanding the Lifespan of Flies
A fly’s lifespan can vary depending on various factors such as species, environment, and overall health. In some cases, flies can live for up to several months, especially in ideal conditions.
It means that even if individual flies do not live very long, their populations can multiply and become a nuisance fast. Maintaining proper sanitation practices and using effective insect control measures to keep fly populations under control is essential.
- Watch Hippo Mother Chases Crocodiles To Protect Her Dead Child - April 15, 2024
- Watch Elephants Ask Rescuer To Play Piano - April 12, 2024
- Top Techniques To Cleaning Up Dog Vomit - April 11, 2024


