Have you ever wanted to know where to see Alligators in the wild? Well clearly you are not the only one.
Interestingly the word “alligator” comes from the Spanish word “el lagarto,” which means “the lizard.” Alligators have lived on Earth for millions of years and are sometimes described as ‘living fossils.’
An alligator is a crocodilian in the genus Alligator of the family Alligatoridae. The two extant species (existing species) are the American alligator and the Chinese alligator.
If you’re interested read ahead or jump to the headline that piques your curiosity!
key points
| Aspect | American Alligator | Chinese Alligator | Extinct Alligators |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Alligator mississippiensis | Alligator sinensis | Various extinct species |
| Length (Adult) | Males: 13 to 15 feet (4 to 4.5 meters) | Males: Up to 5 to 7 feet (1.5 to 2.1 m) | Varies based on species |
| Females: 9 to 10 feet (2.7 to 3 meters) | Females: Slightly smaller than males | ||
| Weight (Adult) | Males: 500 to 1,000 pounds (227 to 454 kg) | Males: 150 to 350 pounds (68 to 159 kg) | Varies based on species |
| Habitat | Freshwater environments: | Freshwater environments: | Varies based on species |
| Marshes, swamps, lakes, rivers, and ponds | Slow-moving rivers, streams, and marshes | ||
| Diet | Fish, turtles, birds, small mammals, | Fish, amphibians, crustaceans, | Varies based on species |
| and other aquatic creatures | and small mammals | ||
| Behavior | Cold-blooded reptiles | Cold-blooded reptiles | Varies based on species |
| Most active during warmer months | Hibernate in burrows during colder months | ||
| Conservation Status | Least Concern | Critically Endangered | Varies based on species |
| (Listed as one of the “precious and | |||
| rare species” in China) | |||
| Notable Fact | Largest reptile in North America | Most endangered crocodilian in the world | Extinct species are known from |
| fossil remains | |||
| Difference between Alligators | Broad, U-shaped snout | Narrow, V-shaped snout | N/A |
| and Crocodiles | (Both are species of genus Alligator) |
Types of Alligators; Lower classifications
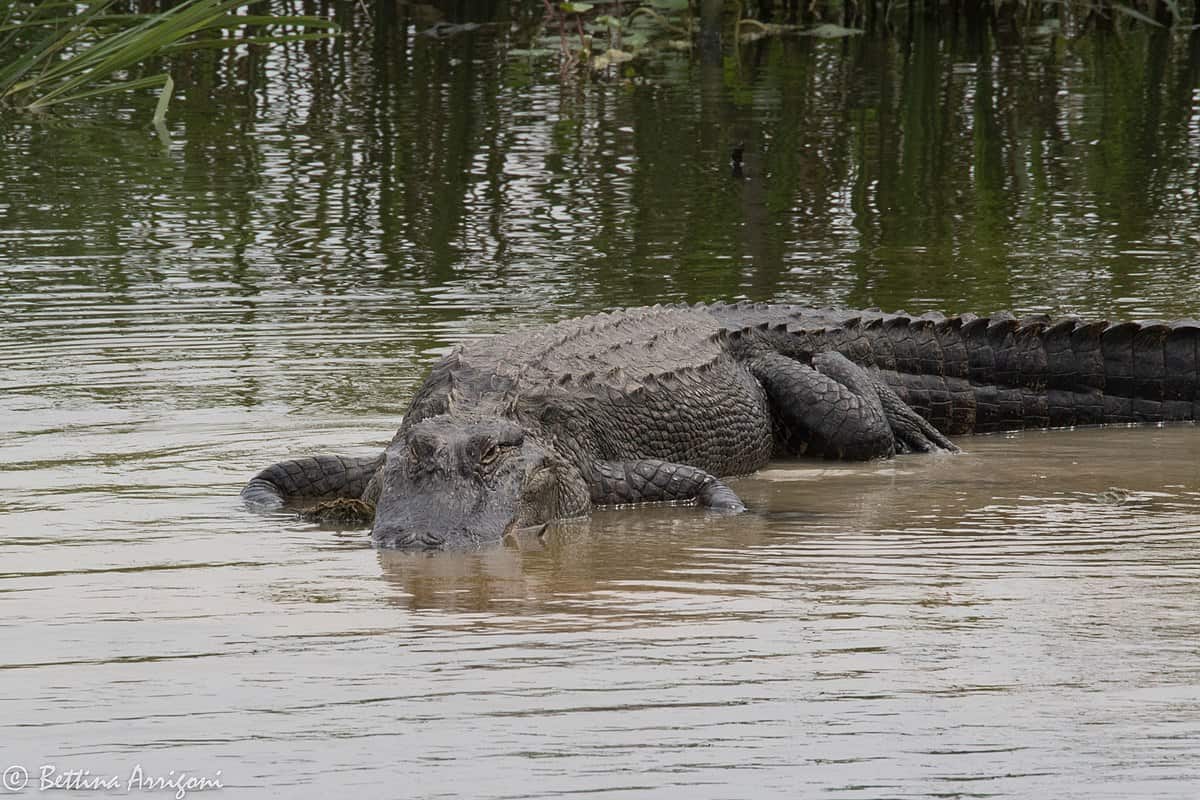

American Alligators

| Aspect | American Alligator |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Alligator mississippiensis |
| Length | Adult males: 13 to 15 feet (4 to 4.5 meters) |
| Females: 9 to 10 feet (2.7 to 3 meters) | |
| Weight | Adult males: 500 to 1,000 pounds (227 to 454 kg) |
| Habitat | Freshwater environments: |
| Marshes, swamps, lakes, rivers, and ponds | |
| Diet | Fish, turtles, birds, small mammals, |
| and other aquatic creatures | |
| Behavior | Cold-blooded reptiles |
| Most active during warmer months | |
| Conservation Status | Least Concern |
The American alligator, sometimes referred to colloquially as a gator or common alligator, is a large crocodilian reptile native to the Southeastern United States, with a small population in Mexico. When young, it exhibits black with yellow marks, while as an adult, it typically exhibits a brownish colour.
Chinese Alligators

| Aspect | Chinese Alligator |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Alligator sinensis |
| Length | Adult males: Up to 5 to 7 feet (1.5 to 2.1 meters) |
| Females: Slightly smaller than males | |
| Weight | Adult males: 150 to 350 pounds (68 to 159 kg) |
| Habitat | Freshwater environments: |
| Slow-moving rivers, streams, and marshes | |
| Diet | Fish, amphibians, crustaceans, and small mammals |
| Behavior | Cold-blooded reptiles |
| Hibernate in burrows during colder months | |
| Conservation Status | Critically Endangered |
The Chinese alligator, recognized by various names, historically the muddy dragon, is a crocodilian species native exclusively to China. The Chinese alligator is a smaller reptile found in China’s Yangtze River area. It resembles its larger counterpart but typically reaches a length of about 1.5 meters, with the highest of 2.1 meters, and features a blackish color with subtle yellowish spots.
The Chinese alligator is considered the most endangered crocodilian globally. It is classified as Critically Endangered on the IUCN Red List, listed in Appendix I of CITES. Fewer than 100 Chinese alligators are thought to remain, and thus the species is considered critically endangered .
You can donate to Chinese Alligator protection via the Chinese Alligator fund.
Extinct: prenasalis Alligators
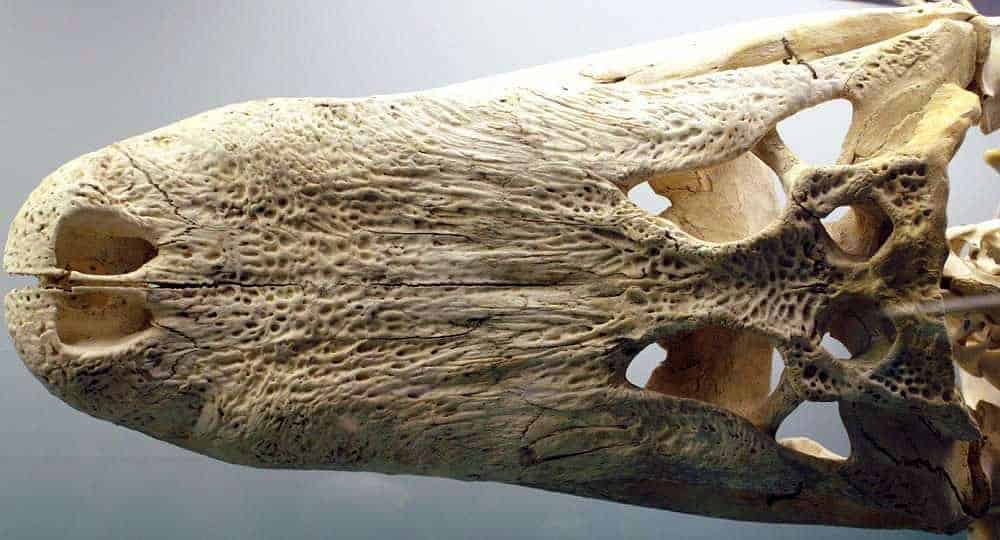
Alligator prenasalise is an extinct species of alligator. It is well known, with many fossils having been collected from the Oligocene Chadron and Brule Formations in South Dakota. The species was first named in 1904, but was originally classified as a crocodile in the genus Crocodilus.
All about Alligators
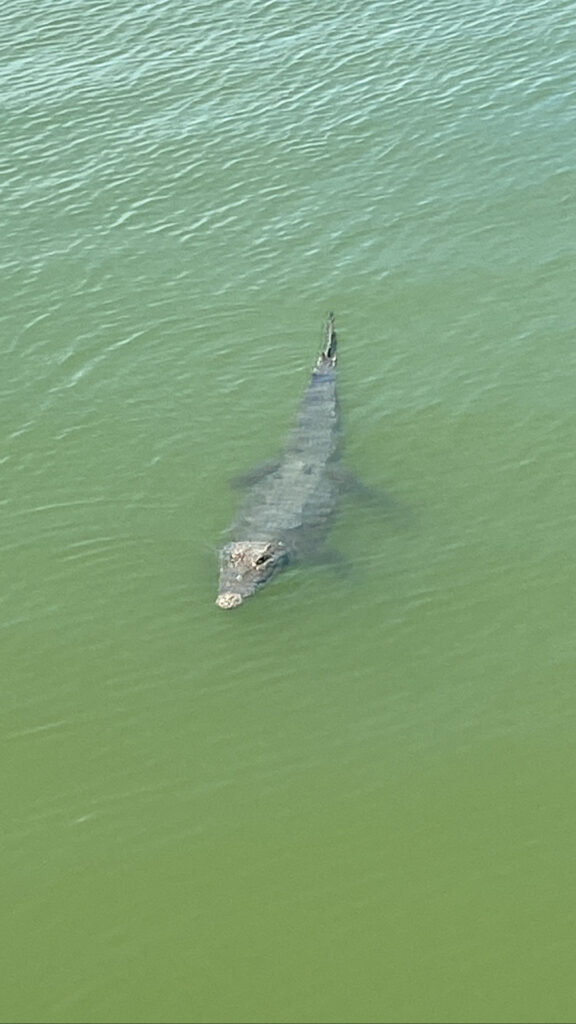

Photo of Alligator in Cancun Mexico. Image via NavyErmine, CC BY-SA 4.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Distribution
America and China. The American alligator is found in the southern United States, ranging from North Carolina to Texas specifically in the Yangtze River basin near the Pacific Ocean. The American alligator inhabits slow-moving rivers, ponds, and swamps, whereas the Chinese alligator, once found in various water bodies, is now mainly restricted to ditches and ponds within agricultural areas.
Habitat
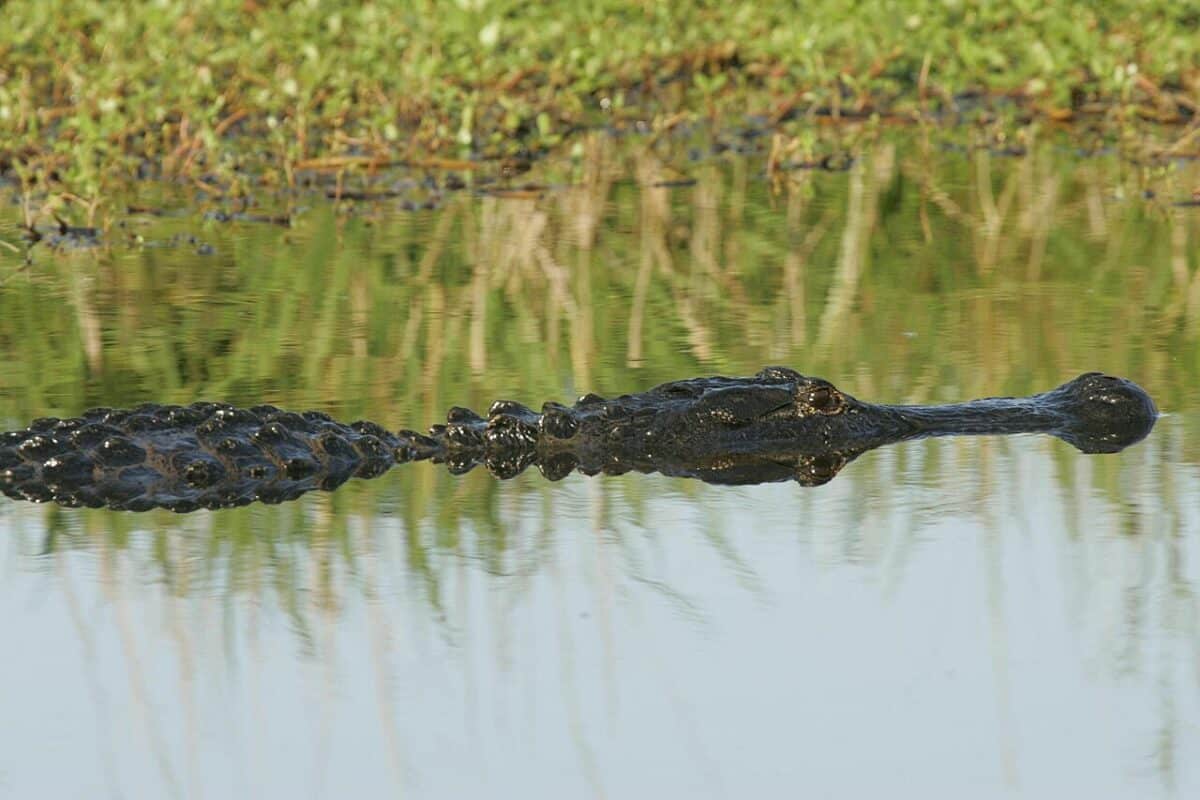

Adult Alligators reign as top predators in their habitat. Their habitat preference leans towards freshwater lakes, slow-moving rivers, and the surrounding wetlands, yet they can also be spotted in brackish water environments.
Diet
The bigger alligators eats mainly fishes, small mammals, and birds but may sometimes take prey as large cattle. Also, alligators eat fruits such as wild fruit directly from trees.
Behavior
Large male alligators are solitary and territorial, while smaller ones can be found in groups. The biggest individuals defend prime territory and smaller alligators are more tolerant of others in their size range.
Alligators are often less dangerous than crocodiles because they are more choosy about their prey.
They exhibit social creatures and often stay in groups called congregations. They are ectothermic, meaning, alligators control their body temperature by basking in the sun, or moving to areas with warmer or cooler air or water temperatures. While most reptiles have 3-chambered hearts, the heart of alligators, and all crocodilians, has 4 chambers, a trait shared with mammals and birds.
Breeding and Lifespan
In breeding season, courtship rituals include head-slapping on the water’s surface, snout and back rubbing, and blowing bubbles. The incubation period spans 65 days. As the eggs near hatching, the juvenile alligators emit high-pitched sounds from within their eggs.
This prompts the mother to excavate them from the nest and transport her offspring to the water in her mouth. She could safeguard her young for about a year.
Average Lifespan is approximately 30-50 years however their have been many alligators living beyond 50 years.
Agility
Alligators utilize water for hunting purposes. While they might appear clumsy on land, their agility in water is remarkable. This aquatic ability significantly enhances their capability to capture prey. American alligators can swim at speeds of up to 20 mph and can run on land as fast as 11 mph.
Communication
Alligators communicate using various calls for territory, distress, competition, and mating. Despite lacking vocal cords, they produce loud bellows by inhaling air and roaring intermittently.
Evolution
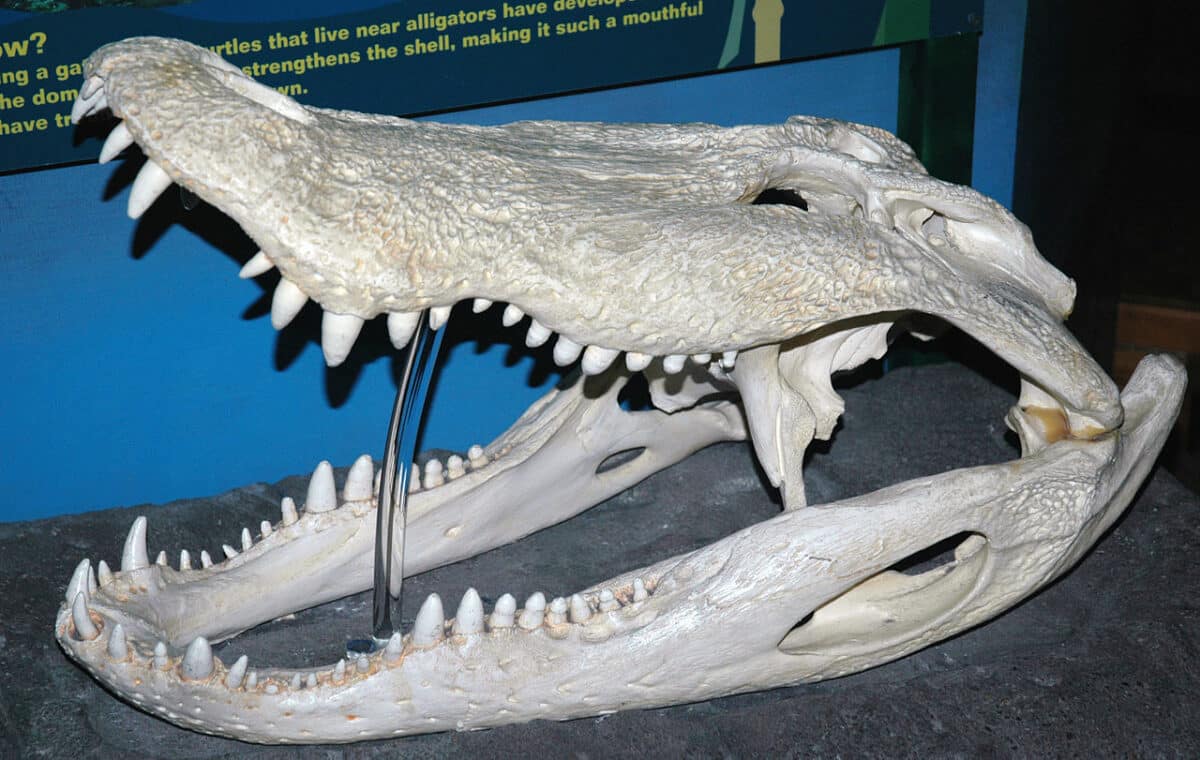

Recent findings suggest that crocodilians, including alligators, share a common ancestor different from the one they have with other reptiles. Despite being classified as reptiles alongside lizards and snakes, alligators are more closely related to birds, whose direct ancestors were dinosaurs.
Conservation status
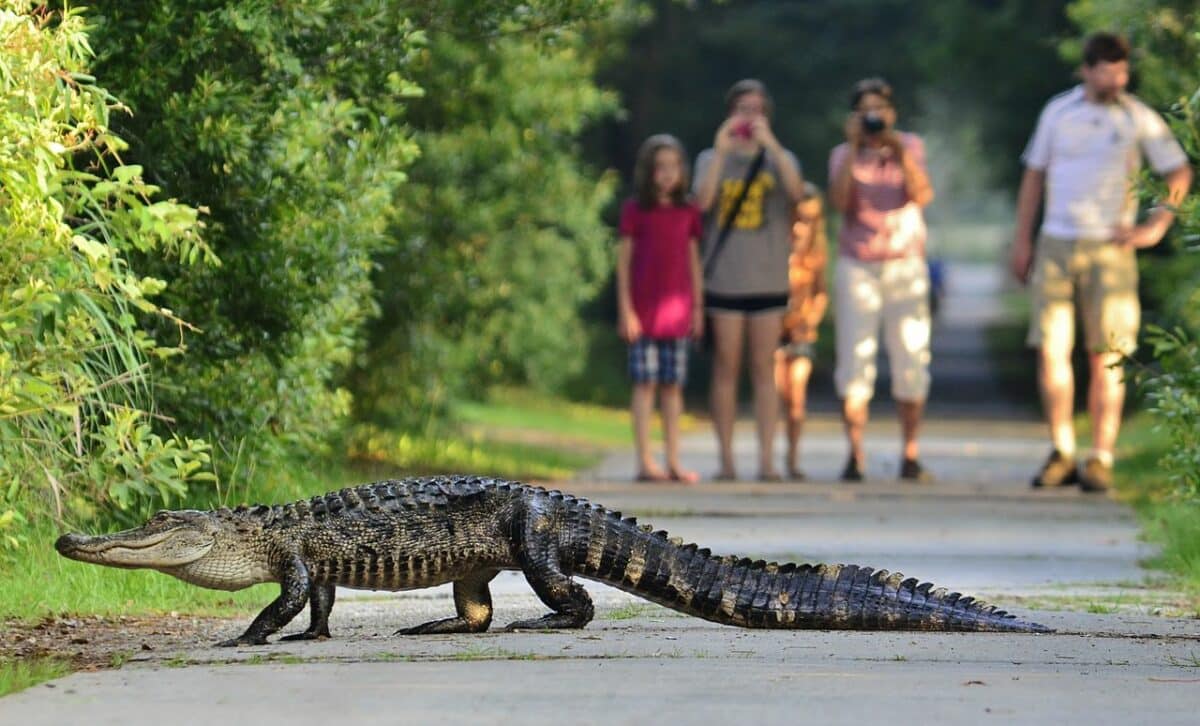

With one of the three types of alligators already extinct, it is deeply saddening to know the Chinese Alligator is crtically endangered. The American alligator faced hunting for its skin, and its young were extensively sold as pets. This led to its decline in many once-populated areas, resulting in legal protection from hunters.
The difference between Alligators and Crocodiles
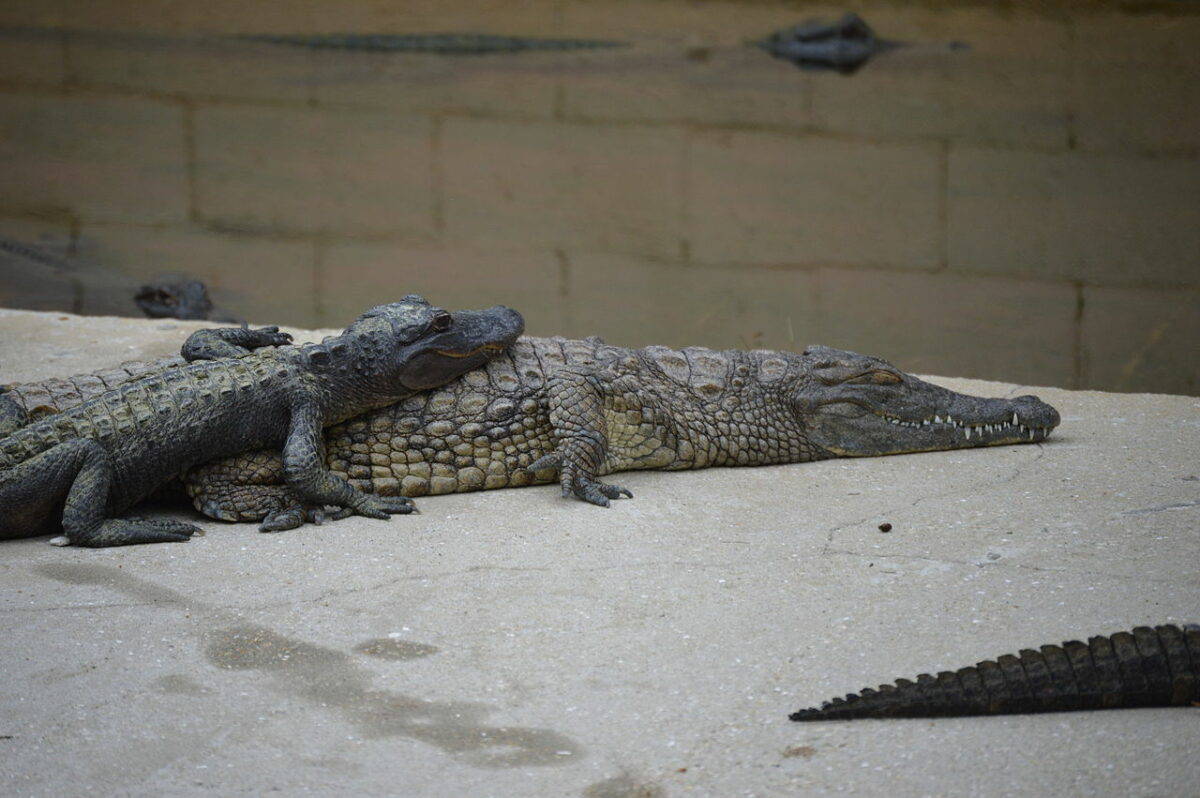

Juvenile American alligator lying on a juvenile American crocodile. Image via Agsftw, CC BY-SA 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Typically, crocodiles are more aggressive than alligators, which makes crocodiles more dangerous than alligators. Alligators are opportunistic feeders. They do not hunt unless it is necessary. However, that certainly doesn’t mean that you should swim with them. Caution should be exercised at all times near alligators and crocodiles.
Crocodile vs alligator snout
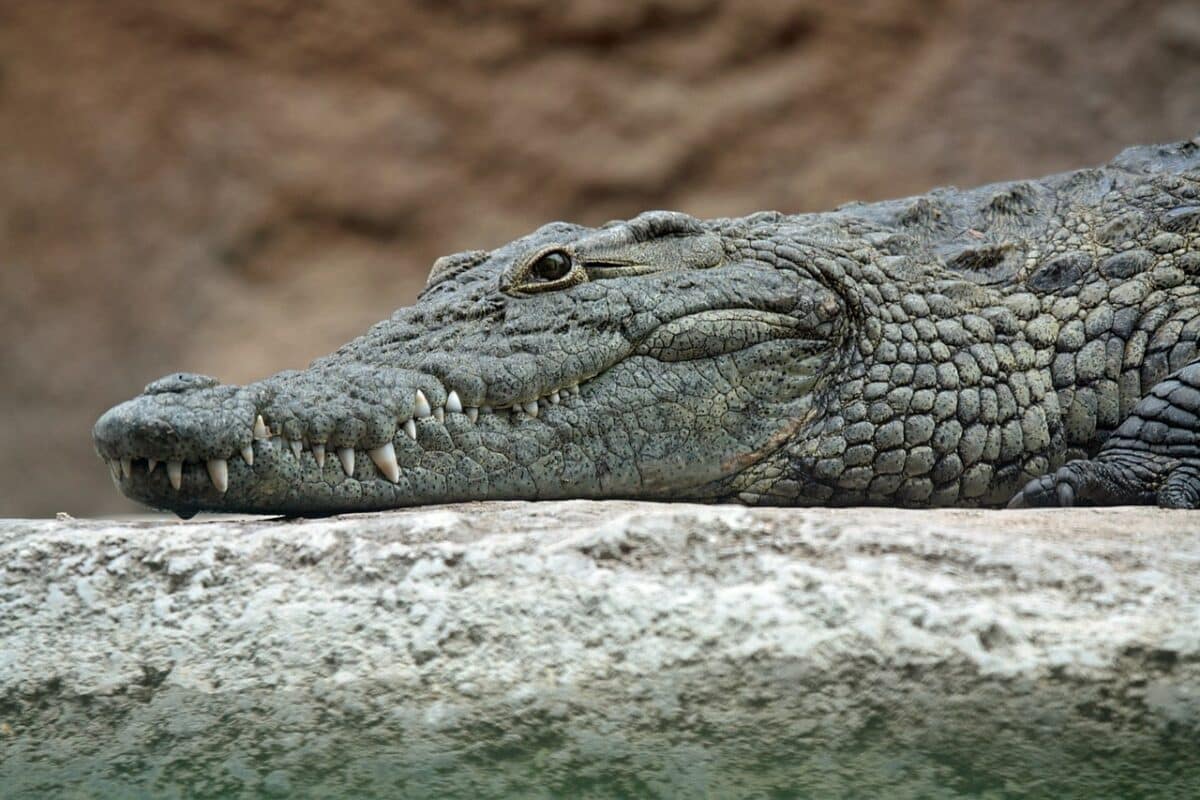

Alligators have a wide, rounded, u-shaped snout, while crocodiles have long, pointed, v-shaped snouts.
Crocodiles are different from alligators in this sense, where both upper and lower jaws of a crocodile are the same size, exposing their teeth as they interlock, creating the look of a toothy grin.
Safety Tips for Alligator encounters
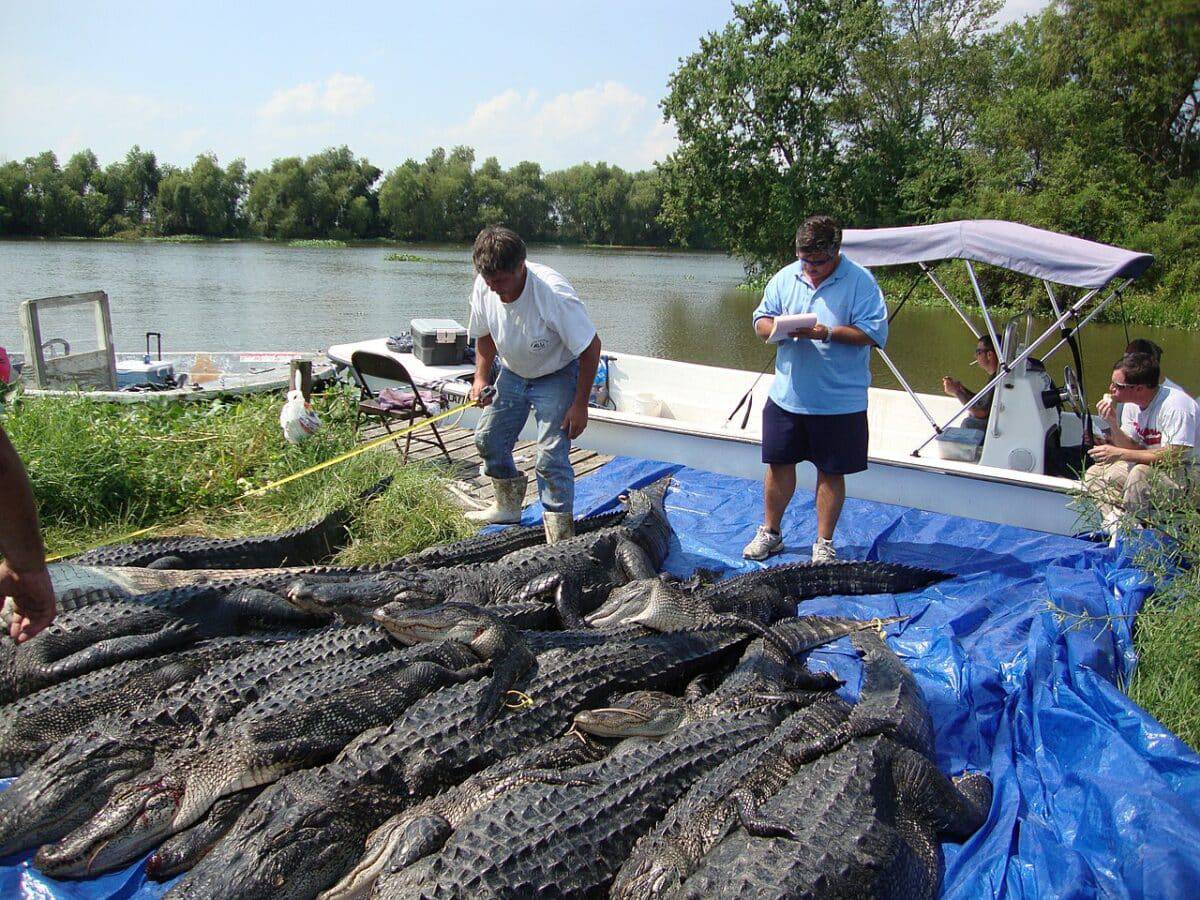

In many coastal regions, humans are encroaching on alligator habitat, so the two species are more likely to cross paths. Population growth and the tourism industry have increased the frequency of human-alligator interactions. It is therefore important to take the following safety precautions…
Alligator Safety
- Leave alligators alone. Alligators are shy animals that usually avoid human contact.
- Pay attention. …
- Do not feed alligators. …
- Throw fish scraps into trash cans. …
- Follow directions on signs. …
- Swim during daylight hours only. …
- Stay with children. …
- Keep an eye on your pets.
If you do have a close run-in with an alligator that charges at you, run away fast and straight, not zig-zag. It is unlikely, however, that an alligator will display this behavior unless you are near its nest.
Where to see Alligators?
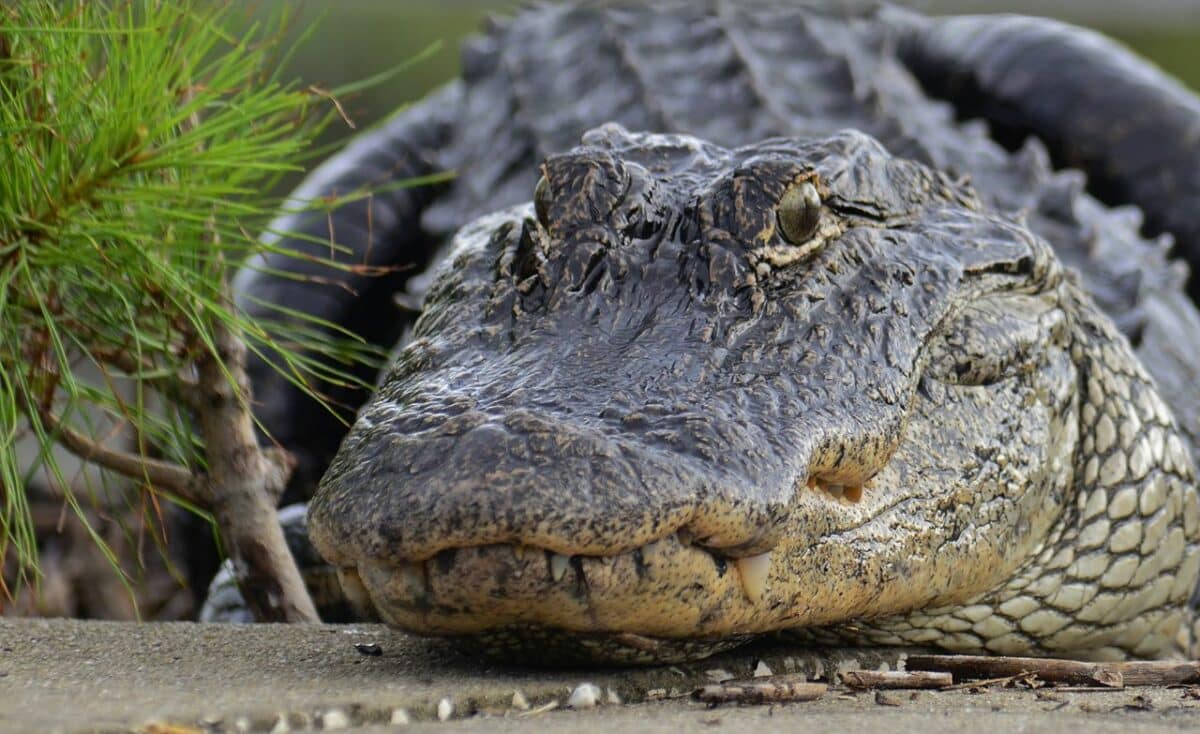

Where to see alligators in America
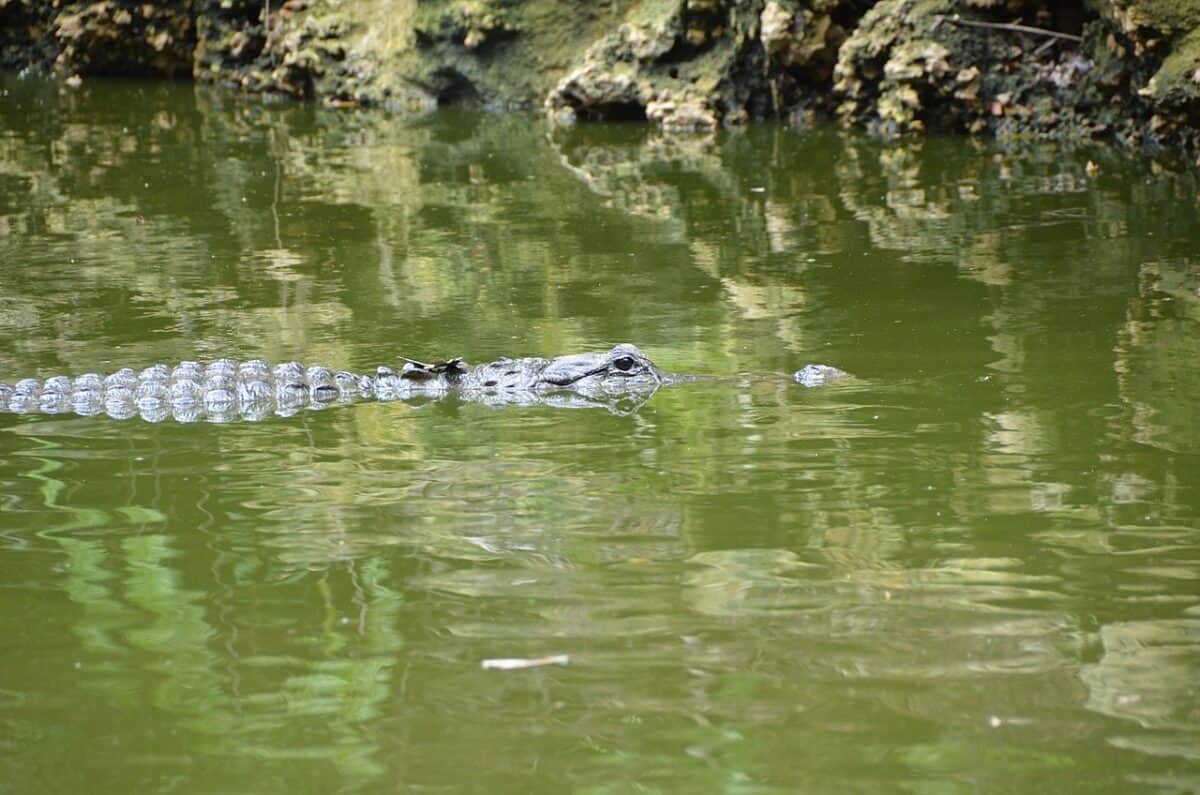

- New Orleans, Louisiana.
- Myrtle Beach, South Carolina.
- The Everglades, Florida.
- Mobile-Tensaw River Delta, Alabama.
- Houston, Texas.
Tours & Operators
Where to see alligators in China
Today it is limited to the lower Yangtze river; the largest river in Asia, primarily in the Anhui and Zhejiang provinces in eastern China. Chinese alligators are found in slow-moving freshwater rivers and streams, including lakes, ponds and swamps.
Unfortunately it isn’t possible to book tours to see these alligators. One can visit alligators in parks across various parts of the country. However we cannot attest to the state of care for alligators. Let us know if you have visited any of these parks and whether or not you can recomend them for alligator encounters…
Where to see Alligators in the Wild: Summary
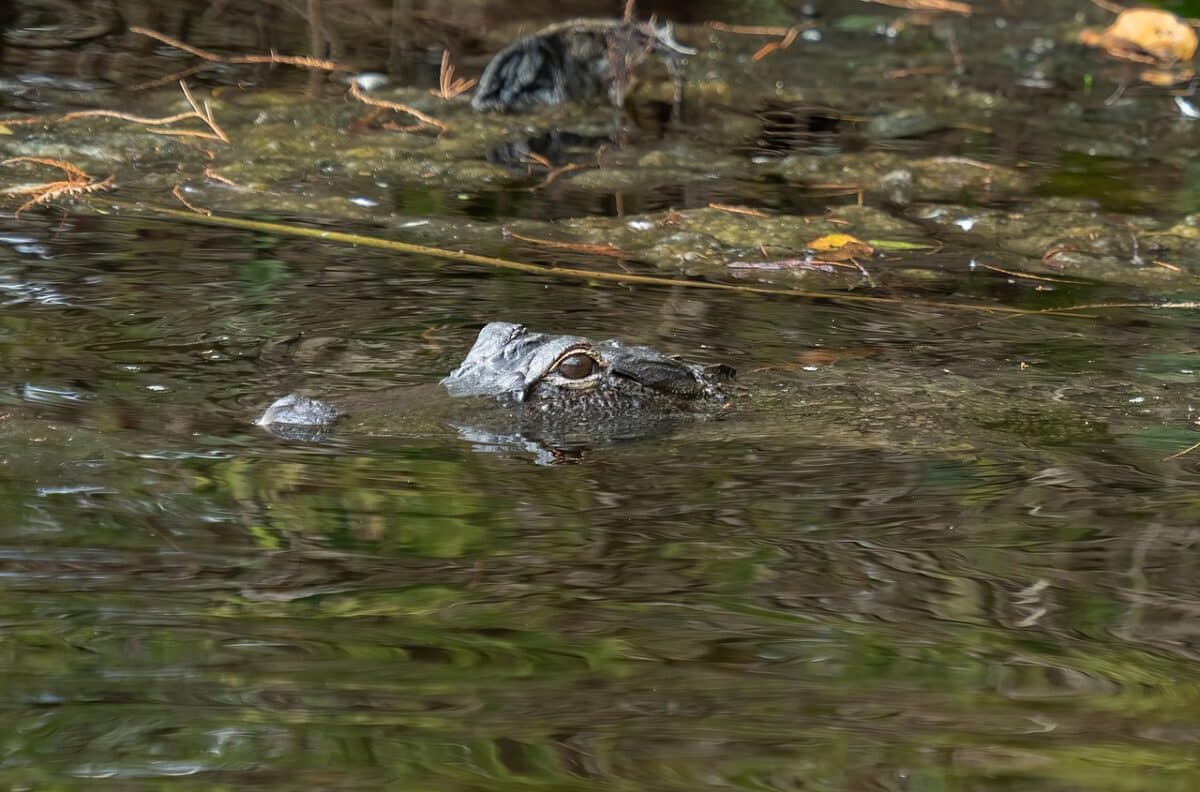

After reading this blog, would you like to see alligators in the wild? It is a privilege to witness the beauty of these majestic and prehistoric reptiles.
Have a look at our other blogs featuring reptiles such as crocodiles and sea turtles!
See ya later Alligator!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Alligators are native to only two countries: the United States and China. The American alligator (Alligator mississippiensis) is found in the southeastern United States, from North Carolina to Texas. The Chinese alligator (Alligator sinensis) is endemic to China, specifically in the Yangtze River region.
No, alligators are not native to Africa. They are found in the United States (American alligator) and China (Chinese alligator). In Africa, you can find different species of crocodiles, such as the Nile crocodile, the African dwarf crocodile, and the West African crocodile.
Yes, alligators are known to be cannibalistic, especially when food is scarce or during territorial disputes. Large alligators may prey on smaller ones, including juveniles or even members of their own species.
Encountering crocodiles in their natural habitat requires caution and adherence to safety protocols. Here are some essential safety measures to consider: maintain distance, observe warning signs, do not swim in unknown waters, stay vigilant during activities and avoid feeding and provoking.
The differences between alligators and crocodiles primarily lie in their physical characteristics, habitat preferences, and behavior. For example, alligators have a wider, U-shaped snout, while crocodiles have a more pointed, V-shaped snout.
Join our Forum for free today!

- These are The 5 Largest Great White Sharks Ever Recorded - July 19, 2024
- The Surprising Benefits of Big Game Hunting - July 18, 2024
- $100k+ Hunting Experiences The Most Expensive Animals to Pursue - July 17, 2024


