Welcome to an in-depth look at Wombat Poop. Dive right in!
Wombat poop, also known as scat, is the feces produced by wombats. It is a unique form of waste that provides essential information about the health and diet of these animals. Wombats are adorable marsupials that are native to Australia.
In this article, we will learn about what these creatures are known for, their burrowing habits, and unique physical characteristics, such as sturdy bodies and powerful hind legs.
Want to jump ahead? Click below
Dietary Habits Of Wombat
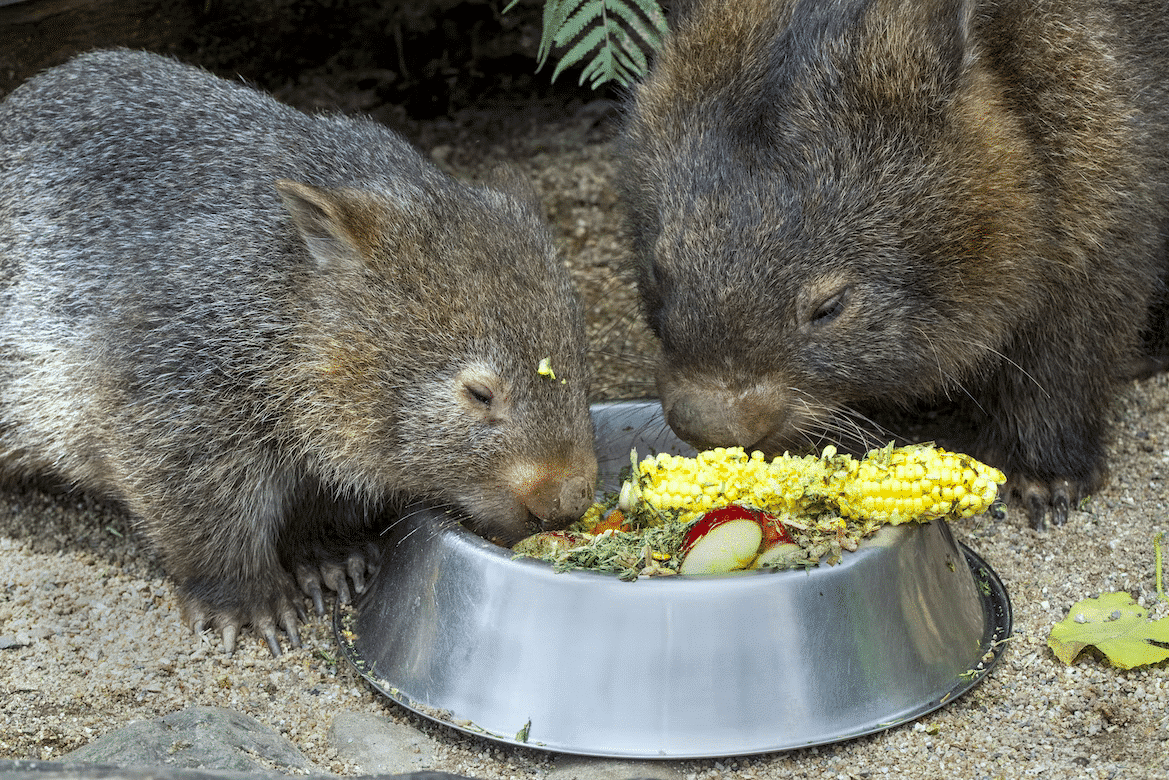
Wombats are herbivorous marsupials native to Australia. They have a specialized digestive system that allows them to digest tough and fibrous plant material efficiently.
The dietary habits of wombats depend on the species and their location. There are three species of wombats: the common wombat, the southern hairy-nosed wombat, and the northern.
Common wombats primarily feed on grasses, sedges, herbs, and the roots, bark, and leaves of shrubs and trees. They use their strong front teeth and powerful jaws to break down tough plant material. They are known to graze for up to four hours a day.
Wombats have a slow metabolic rate, which means they have a low energy requirement. They can extract more nutrients from their food than other herbivores because of their specialized digestive system. They have a long digestive tract, which allows them to ferment the plant material in their hindgut, breaking down cellulose and extracting more nutrients.
The dietary habits of wombats consist of various tough plant materials, with a preference for grasses, sedges, and herbs. Their specialized digestive system allows them to efficiently extract nutrients from their food and survive on a low-energy diet.
Common Wombat
The largest species of wombat, the common wombat, is indigenous to the southeastern region of Australia. This sturdy and leisurely mammal is recognized for its remarkable burrowing capabilities. With a thick and compact coat, the common wombat is well-equipped to endure various weather conditions. Its muscular hind legs and formidable claws enable it to excavate burrows adeptly.
Wombat’s poop is cube-shaped and about 2 cm wide. It is one of the mammals that excrete cube-shaped feces, which helps to prevent it from rolling away from its burrow entrance. This poop is made of tough and fibrous material, resulting from the wombat’s vegetation diet.
Southern Hairy-Nosed Wombat
This wombat is found in south and southeastern Australia. It is known for its distinctive hairy nose and social behavior, as these wombats live in large groups. The southern hairy-nosed wombat has a lighter and softer coat than the common wombat and is also a slower burrower.
It is more round than cube-shaped but still relatively firm and fibrous. This poop is also the result of its diet of tough vegetation and is similar in composition to the poop of the common wombat.
Northern Hairy-Nosed Wombat
The northern hairy-nosed wombat is the rarest wombat species in the wild. It is a large, stocky animal with a dense, shaggy coat and is also a skilled burrower known to dig complex burrow systems.
It is similar in composition to the ordinary and southern hairy-nosed wombats, but it is slightly larger and more elongated in shape. Like the other two species, this poop is made of tough and fibrous material and results from the wombat’s diet of tough vegetation.
Each species of wombat has unique characteristics and features, and their poop is no exception—the cube-shaped poop is of the common wombat, and the round poop is of the southern hairy-nosed wombat.
The long poop of the northern hairy-nosed wombat is all the result of their tough diets and the adaptations that have evolved to help them survive in their respective habitats. If you ever have the opportunity to observe these amazing creatures in the wild, take a closer look at their poop and see how it reflects their unique biology and adaptations.
wombat poop is an essential component of the ecosystem and provides valuable insights into the behavior and biology of these creatures. As research uncovers the many benefits of wombat poop, its use and importance will likely grow.
Future research should focus on identifying new ways to utilize wombat poop and its benefits, as well as exploring its potential impact on the ecosystem and the health of the wombat population.
Additionally, continued research on the composition of wombat feces and its role in soil fertility will be crucial in understanding this unique waste form’s full significance.
Importance Of Studying Wombat Poop

The study of wombat poop is essential for several reasons:
- Understanding Wombat Health And Diet
Wombat poop provides valuable insights into the health and diet of these marsupials. Changes in the composition and quantity of their feces can indicate the presence of disease or changes in their eating habits.
- Ecosystem Monitoring
Wombats play a unique role in their ecosystems, and their poop helps assess their impact on their surroundings. Scientists can better understand how wombats shape their habitats by analyzing the nutrients and microbes in wombat poop.
- Conservation
Wombats are threatened by habitat loss and disease, and studying their poop can help inform conservation efforts. For example, if changes in their diet or health are detected, conservationists can take steps to address the underlying issues.
- Fertilizer
Wombat poop is high in nitrogen and phosphorus, making it an essential fertilizer for plants in their habitats. Understanding the nutrient content of wombat poop can help to inform land management practices and maximize the benefits of this special fertilizer.
- Scientific Advancement
Studying wombat poop is also essential for advancing the diversity of life on Earth. By analyzing the microbes in wombat poop, scientists can gain insights into the relationships between different species and their roles in ecosystems.
Overall, the study of wombat poop provides valuable information for improving our understanding of these unique animals and their ecosystems, as well as for conservation efforts and land management practices.
Check out 15 Animals Who Help the Environment and How They Do It.
Study Methods For Wombat Poop
- Collection
Wombat feces is collected for study using various methods, including direct observation, trapping, and remote camera monitoring. The most important consideration when collecting samples is minimizing contamination and ensuring the feces represent the wombat’s diet and health.
- Preservation
It must be stored and preserved appropriately to ensure the feces remains suitable for analysis. It typically involves freezing the samples immediately after collection, which helps protect the feces’ microbial and chemical composition. In some cases, preservatives such as ethanol or formalin may stabilize the samples further.
Analysis Techniques For Wombat Poop

- Chemical Analysis
Firstly, chemical analysis of wombat feces is used to determine the nutrient content and composition of the feces. This information is essential for understanding the role of wombats in their ecosystems and the nutrients they provide to other species. Standard chemical analysis techniques include proximate, mineral, and isotope analysis.
- Microbial Analysis
Secondly, analysis of wombat feces is used to identify the variety of microbes present in the feces and to understand the role they play in the ecosystem. It can be done through various techniques, including culture-based methods, DNA sequencing, and metagenomics.
- DNA Analysis
DNA analysis of wombat feces is used to identify the species of plants and animals that the wombat has consumed. This information is important for understanding the wombats’ diet and its impact on their habitats. DNA analysis can be performed using various techniques, including PCR, high-throughput sequencing, and stable isotope analysis.
Importance of Controlled Conditions

- Standardized Collection and Preservation Methods
Using standardized collection and preservation methods is essential for ensuring that the results of wombat feces studies are accurate and consistent. It requires careful control of variables such as time of collection, temperature, and preservation method.
- Controlling For Environmental Variables
Environmental variables, such as temperature, precipitation, and soil type, can significantly impact the composition of wombat feces. Therefore, it is essential to control for these variables in wombat feces studies to ensure that the results accurately represent the wombat’s diet and health.
Replication In Studies

Undeniably, replication is essential to controlled conditions in wombat feces studies. By repeating studies multiple times under controlled conditions, researchers can validate their findings and minimize the impact of extraneous variables.
- The Significance Of Wombat Feces
Wombat poop, also known as scat, is a unique and important aspect of the ecosystem and plays several significant roles. Some of these include:
- Nutrient Recycling
Markedly, wombat scat contains plant material and other organic matter that serves as a source of nutrients for other organisms in the ecosystem.
- Soil Enrichment
Likewise, the scat of wombats is high in calcium carbonate, which helps to increase soil fertility and improve soil structure.
- Marking Territory
Notwithstanding, wombats mark their territory and communicate with other wombats with their scat. Their scat’s distinctive shape and smell help to establish dominance and warn off potential intruders.
- Biodiversity
Nonetheless, wombat scat provides a habitat for various insects, fungi, and other microorganisms, which helps maintain biodiversity in the ecosystem.
Physical Characteristics Of Wombat Feces

- Shape And Dimensions
Wombat feces is generally oval-shaped, and its dimensions are comparable to golf balls. It measures 2-3 centimeters approximately.
- Color And Consistency
Secondly, wombat feces typically appear dark brown and have a thick, chunky consistency. While it is often compared to dog feces in appearance, it tends to be coarser and drier than the latter.
- Texture
Particularly, the texture of wombat feces is often described as dense, dry, and compact.
- Odor
Wombat feces exudes a distinctive, earthy odor that can be compared to the scent of damp soil or mushrooms. The odor is not overpowering, but it is noticeable and can be used to track the presence of wombats in the wild.
Composition Of Wombat Poop

The composition of wombat poop is unique and an essential indicator of the wombat’s diet and digestive process. Wombat scat is generally:
- Cube-Shaped
Firstly, this shape is created by the muscular action of the wombat’s intestines and rectum, which helps the scat stack neatly, minimizing the amount of space it takes up.
- Dry And Fibrous
Wombat scat is usually dry and fibrous due to the low-moisture diet of the wombat and its slow digestive process.
- High In Calcium Carbonate
Wombat scat is high in calcium carbonate, which helps maintain the wombat’s bone density. The high calcium carbonate concentration also helps improve soil fertility and structure.
- Low In Nitrogen
Fourthly, wombat scat is low in nitrogen, a characteristic of herbivores. It reflects the wombat’s diet of tough, fibrous plants.
- Nutritional Value
Lastly, wombat poop is not a commonly consumed food item and is not considered a source of human nutrition. Additionally, consuming wombat scat can harm your health as it may contain parasites, bacteria, and other pathogens that can cause illness.
Health Implications Of Consuming Wombat Poop

Wombat poop is not a commonly consumed food item and is not considered a source of nutrition for humans. While it may be tempting to try something different, it’s essential to understand the potential health risks associated with consuming feces. In this section, we will discuss the presence of parasites, bacteria, and pathogens in wombat scat and the health risks associated with consuming feces.
- Presence Of Parasites, Bacteria, And Pathogens
Undoubtedly, wombat scat can contain a variety of harmful parasites, bacteria, and pathogens that can cause illness if consumed.
These can include harmful bacteria like E. coli, Salmonella, and Campylobacter and parasites like tapeworms, roundworms, and Giardia.
Additionally, these organisms can cause various health problems, including stomach cramps, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and even fever.
- Health Risks Associated With Consuming Feces
Unquestionably, the risk of exposure to these contaminants increases if the wombat consumes food or water contaminated with pollutants or chemicals.
Ecological Significance Of Wombat Poop

Role In Soil Fertility: Firstly, wombat poop plays a vital role in maintaining soil fertility by adding essential nutrients back into the soil. Additionally, the physical presence of wombat burrows can help to aerate the ground, improving its overall structure and fertility.
Food Source for Other Species: Surprisingly, some animals feed on wombat poop, which helps break down the feces and distribute its nutrients back into the soil, supporting the growth of new plants and contributing to the ecosystem’s health.
Enhancing Ecosystem Diversity: Wombat feces are essential in sustaining a diverse range of species in the ecosystem. This diversity is crucial for the stability of the ecosystem and helps protect against potential threats such as disease or environmental changes. Presently, by providing food and vital nutrients to different species, wombat feces contribute to the richness of the ecosystem and its ability to persist and thrive.
Wombat Poop And Human Interaction

Because the dense, compact nature of the feces made it burn slowly and produce consistent heat, indigenous people in Australia used wombat poop as fuel for fires in the past.
Evidently, today, wombat poop is used in science and research to study the health and diet of these creatures. Scientists and researchers can analyze the composition of the feces to determine what the wombats have been eating.
Future Potential Of Wombat Poop

Surprisingly, wombat poop can be used in various ways in the future, as research uncovers the many benefits of wombat poop, its use and importance will likely continue to grow.
This animal’s poop is a unique form of waste that provides important information about the health and diet of these creatures. It has physical characteristics such as being oval-shaped and dark brown and is composed of a mixture of plant matter and undigested material. It also has ecological significance, playing a role in soil fertility and serving as a food source for other species.
Wrapping up with Wombat Poop
In conclusion, while it may not be the most glamorous topic, wombat poop is a fascinating and vital ecosystem component that deserves further attention and study. Wombat poop is a unique form of waste that provides essential information about the health and diet of these creatures.
It has physical characteristics such as being oval-shaped and dark brown and is composed of a mixture of plant matter and undigested material. It also has ecological significance, playing a role in soil fertility and serving as a food source for other species.
Thanks for following along with us. If you enjoyed this, you might want to take a look at Alligator Poop.
Join our Forum for free today!

- Big Cats Love Mouthing Affection - July 22, 2024
- Kind Elephant Merciful To Lion Cubs - July 22, 2024
- Beachgoers Save Massive Shark Stranded In Florida - July 22, 2024


