Snakes are limbless reptiles that belong to a suborder called Serpentes. They are often antagonized, seen as villains that tempted Eve to eat the apple in the garden of Eden, or dangerous creatures that threaten human lives. For the most part, however, snakes are misunderstood. Only about 20% of snakes are venomous, and less than 7% of species pose any real threat to humans.
Venomous snakes use their venom to subdue and kill prey, but rarely as a self-defense tactic. Snakes that are non-venomous kill their prey by constriction or swallow live prey whole.
The oldest snake fossils found are between 112 and 94 million years old, which dates their evolution to the Late Cretaceous Period.
Snakes Overview

50 Species of Snakes
- African puff adder
- American copperhead
- Asp viper
- Ball python
- Banded krait
- Banded pit viper
- Black mamba
- Black-necked spitting cobra
- Boa constrictor
- Boomslang
- Brazilian smooth snake
- Burmese python
- California kingsnake
- Cape cobra
- Chicken snake
- Common garter snake
- Common lancehead
- Common tiger snake
- Coral snake
- Cottonmouth
- Eastern coral snake
- European asp
- Golden tree snake
- Grass snake
- Great Lakes bush viper
- Green anaconda
- Green mamba
- Horned viper
- Inland Taipan
- Japanese rat snake
- King cobra
- Mangrove snake
- Mojave rattlesnake
- Northern tree snake
- Northern water snake
- Queen snake
- Rainbow boa
- Red-bellied black snake
- Reticulated python
- Rinkhals
- Sand boa
- Texas night snake
- Texas rat snake
- Tiger snake
- Timber rattlesnake
- Water moccasin
- Western blind snake
- Western Diamondback rattlesnake
- Yellow-bellied sea snake
- Zebra snake
Learn more about rattlesnakes here!
How Many Species Are There?

There are over 3,000 species of snakes worldwide. Snakes can be found in most countries, except Antarctica and, interestingly, Iceland, Ireland, Greenland, and New Zealand.
Where Do They Live?
Snakes can be found in almost any habitat, even in your backyard! They are typically found alone, either hunting for food, which is when they are their most dangerous, or lying on a rock to bask in sunlight. They are most commonly found in the following environments:
- Forests
- Deserts
- Grasslands
- Rocky mountains
- Fresh water
- Salt water
Learn More About Snakes
-

How Sea Snakes Breathe While Living in the Ocean
-

The Most Venomous Snakes Slithering Through the Backwoods of Alabama
-

9 Habitats Snakes Thrive In And 3 They Slither Away From
-

How to Survive a Snake Encounter in the Wild
-

The Secret Diet of the Worlds Largest Snake and How It Swallows Prey Whole
-

The Largest Anaconda Ever Spotted in the Amazon
Well-Known Snakes
| Scientific classification | Habitat range | Feeding | Examples | |
| Anaconda | 5 species; genus Eunectes; type of boa | Tropical South America | Constrictors | Green anaconda; yellow anaconda |
| Boa | 54 species; family Boidae | Americas, Africa, Europe, Asia | Constrictors | Boa constrictor; rainbow boa |
| Cobra | 38 species; genus Naja | Africa, Asia | Venomous | King cobra; American cobra |
| Mamba | 4 species; genus Dendroaspis | Sub-Saharan Africa | Venomous | Black mamba; Jameson’s mamba |
| Python | 10 species; genus Python | Africa, Eastern Asia | Constrictors | Burmese python; blood python |
| Viper/Adder | 92 species; subfamily Viperinae | Africa, Asia, Europe | Venomous | Puff adder; Sahara sand viper |
Types of Snakes
Rattlesnakes
You hear these majestic snakes just before you see them. Then turn around to see a rattlesnake – long and scaly, willing to use their venom in defense when feeling threatened. Learn more about these incredible reptiles by clicking on any of the images below or heading over to our dedicated rattlesnakes page.
-

Rattlesnakes of San Francisco
-
Terrifying Encounter Between Man and Eastern Diamond Rattlesnake (Video)
-

The Toxic Timber Rattlesnake Bite
-

Colorado’s Rattlesnake Den Livestreams 2,000 Snakes
-

The Largest Rattlesnakes Ever Caught—Massive Serpents Spreading Across the U.S.
-

Researchers Install Live Webcam in Colorado’s Largest Rattlesnake Den (Over 2000 Snakes)
-

Florida Influencer Survives Rattlesnake Bite—88 Vials of Anti-Venom Needed
-

California Man Receives Live Rattlesnake in Mail, Suspects Attempted Murder
-

Rare and Highly Toxic Eastern Massasauga Rattlesnake Found in Ohio
Well-Known Snakes Images
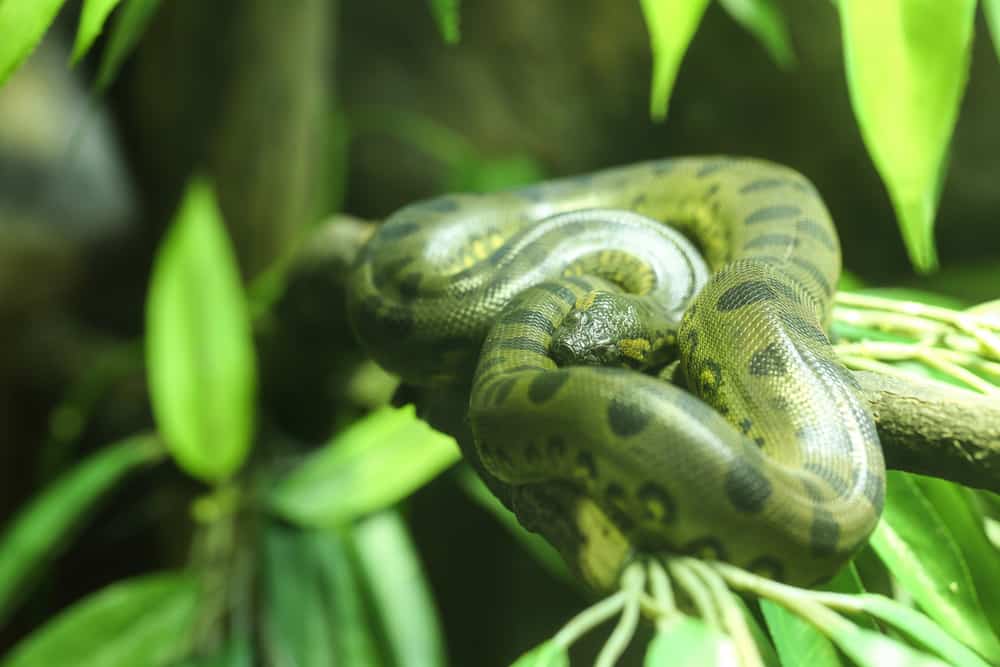
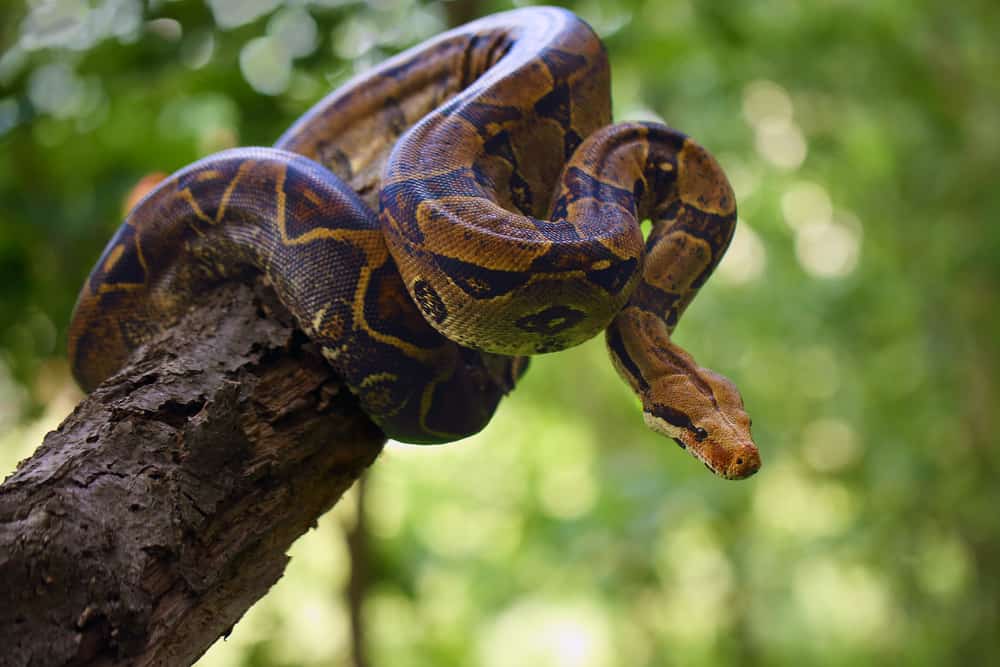
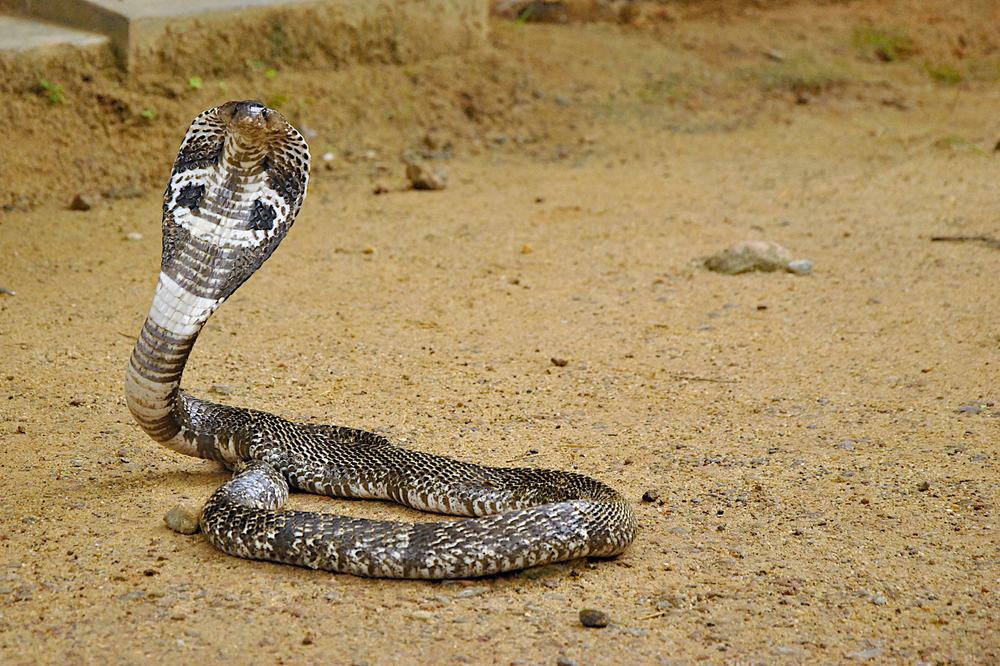
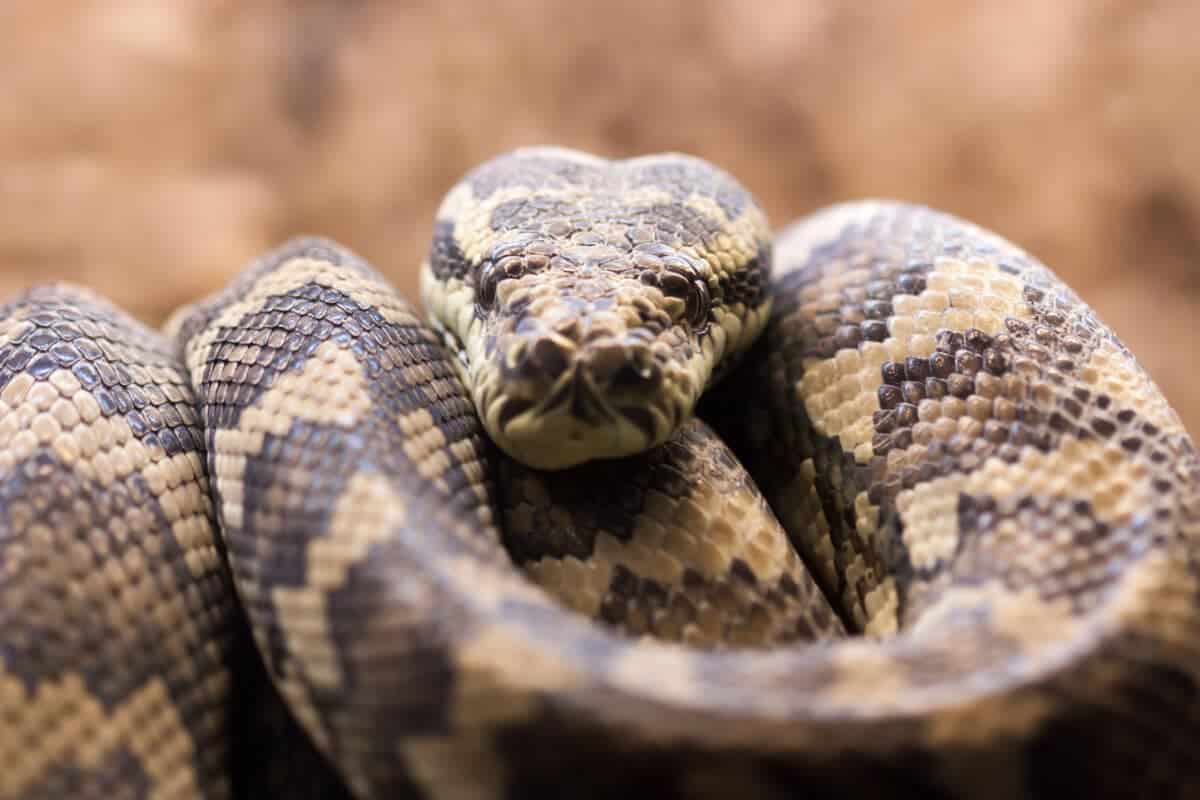
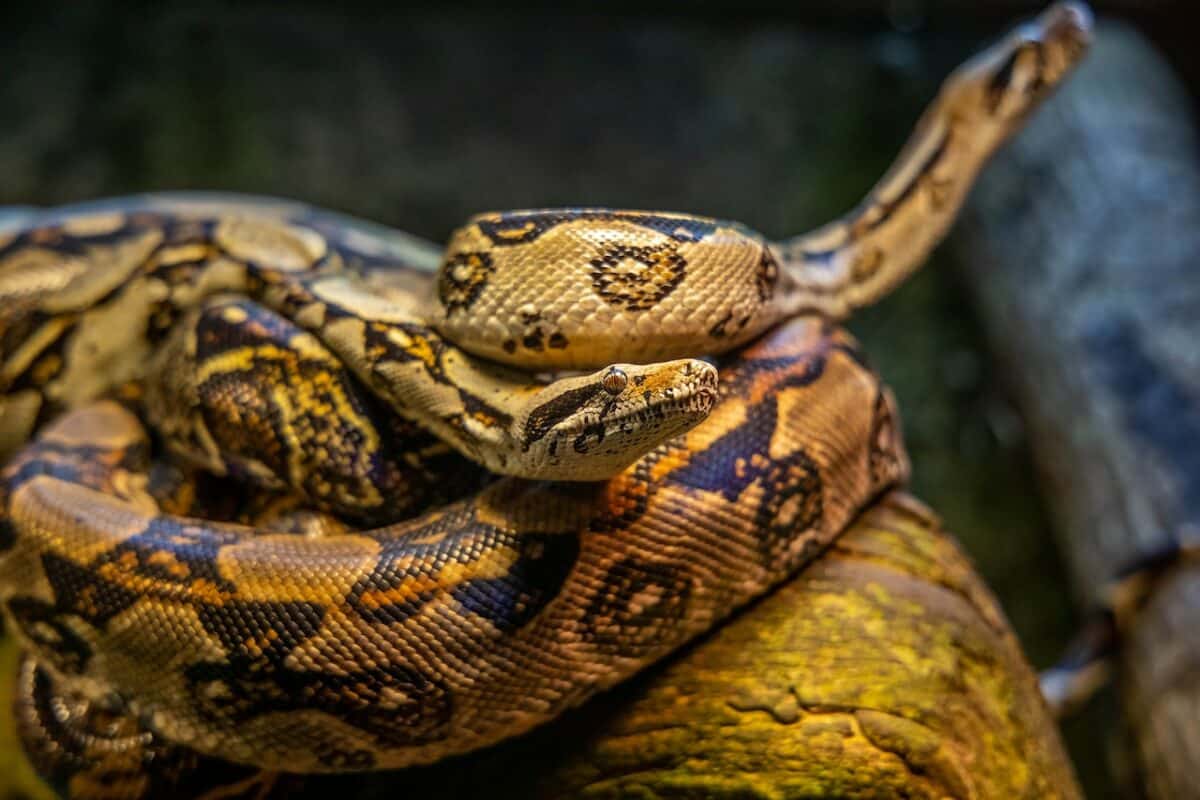






Learn More About Pythons
Difference Between Venom and Poison
Simply put, something is venomous if it bites you and you are harmed, but poisonous if you bite it and you are harmed. Snakes are venomous, whereas belladonna is poisonous.
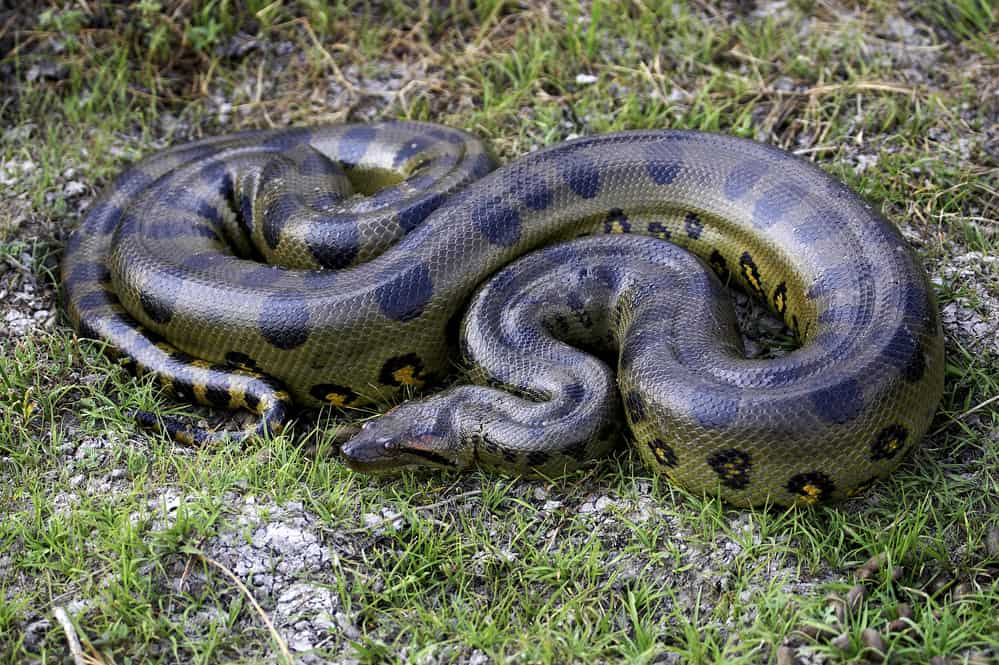
Largest vs. Smallest Snake by Weight
| Green anaconda | Barbados threadsnake | |
| Scientific name | Eunectes murinus | Tetracheilostoma carlae |
| Body size | Up to 440 lb (200 kg); 26 ft (8 m) | 0.02 oz (0.6 g); 4 in (10 cm) |
| Habitat range | Southeast South America | Barbados & Anguilla |
| Diet | Fish, amphibians, birds, small to medium-sized mammals | Termites, ant larvae |
| Conservation status | Least concern | Critically endangered |


7 Fun & Surprising Facts
- Snakes don’t have any eyelids; instead, they have brilles, which are like clear scales that protect their eyes.
- Snakes have very flexible jaws that allow them to swallow prey much larger than themselves.
- Snakes use their tongues to smell using a specialized organ called the Jacobson’s organ.
- Snakes are ectothermic, meaning they cannot regulate their body temperature internally and instead rely on the sun to keep warm.
- Snakes shed their skin periodically to remove parasites and dead skin cells.
- All snakes have forked tongues.
- Despite their often negative portrayal in popular culture, snakes are essential members of ecosystems and deserve our respect and protection.
Snake News
-

An Animal Comparison: Hippo vs Cobra
-

Eagle vs. Cobra
-

Milk Snake vs Spitting Cobra
-

Rattlesnake Bite Forces Teen’s Airlift From North Carolina Forest
-

12 Extraordinary Facts About Snakes That Most People Don’t Know
-

The 10 Most Snake-Infested Lakes and Rivers in the U.S.—And Why Their Numbers Are Exploding
-

The Tale of an Epic Battle Between a Cobra and a Rhino
-

Discover How Dangerous is a Horned Viper Snake Bite?
-

Largest Gaboon Viper Caught on Camera
-

8 Snakes That Are Completely Harmless to Humans
-

The Epic Showdown Between a Tiger and a Cobra
-

The 8 Most Popular Snake Species Across the USA
Snake FAQs
All snakes are carnivores. They consume a variety of small to medium-sized animals including rodents, birds, reptiles, fish, amphibians, and eggs.
Snakes communicate with each other by means of pheromones, which are chemical substances that many animals can secrete via the vomeronasal organ, also known as Jacobson’s organ. Pheromones are used to attract mates and warn others against danger. Snakes can also communicate using sounds, such as hissing; however, they don’t communicate with each other this way and will only hiss as a warning signal for another creature, including humans.
The snake that has caused the most human deaths is the saw-scaled viper (Echis carinatus). This snake can be found in the Middle East and central Asia. These snakes are responsible for at least 5,000 deaths every year; although its venom is only lethal if the victim is not administered antivenom soon enough.
Snakes evolved not to need them. There is evidence that the ancestors of snakes lived in burrows underground, so it’s thought that these reptiles required the use of their limbs less to move around their terrestrial environments. They evolved without bones like those in the pelvic girdle, and instead developed more spinal bones.
Snakes maintain balance in ecosystems by controlling populations of smaller animals like rodents. These smaller animals can become pests in their environments as they often produce large numbers of offspring, carry diseases, and consume a lot of vegetation.
Animals that hunt, kill, and eat snakes include raptors like eagles, mongooses, honey badgers, coyotes, and even other snakes like the King cobra.
Latest in Snake Conservation
Many snake species are at risk of extinction due to factors like habitat loss and illegal trade. Additionally, a major threat to the survival of these keystone species is the indiscriminate killing by people who misunderstand them. Humans often disdain snakes due to fear, superstitions, or perceptual biases.
Accordingly, snake conservation efforts are crucial for educating people about the importance of snakes in ecosystems as natural pest controllers, for dispelling the myths around the dangers of snakes, and for their effective management when they come into yards or houses. Snake conservation organizations also advocate for the protection and restoration of habitats where snakes are found.
Save the Snakes and Center for Snake Conservation are two such organizations.
Snakes as Symbols
Snakes are one of the most widespread symbols across religions and cultures throughout human history. They are thought to be so significant to us because we, as primates, were once seriously threatened by snakes. This may explain why ophidiophobia is one of the most common phobias among people.
One of the oldest symbolic representations of snakes is the caduceus, which dates back to around 3,000 BCE in ancient Mesopotamia. The caduceus (pronounced kah-doo-see-uhs) is the symbol of a staff entwined with two snakes, used in modern times to represent anything medicine-related. Interestingly, the caduceus was also the staff carried by Hermes in Ancient Greek mythology. This use dates back to around 1,000 BCE.

Aesthetically, snakes make great tattoo designs because their form can be manipulated in versatile and artistic ways. For this reason and because of the complex and deep symbolism associated with snakes, as well as their being misunderstood creatures, they are an incredibly popular tattoo subject. I might even get a snake tattoo myself after writing this.
Learn more about other reptiles:
Newest Category: Snakes
- Discover: Animals Can Catch Yawns - June 26, 2025
- The Fascinating World of Hybrid Animals - June 24, 2025
- Wild Animals React to Seeing Themselves in Mirror - June 22, 2025

