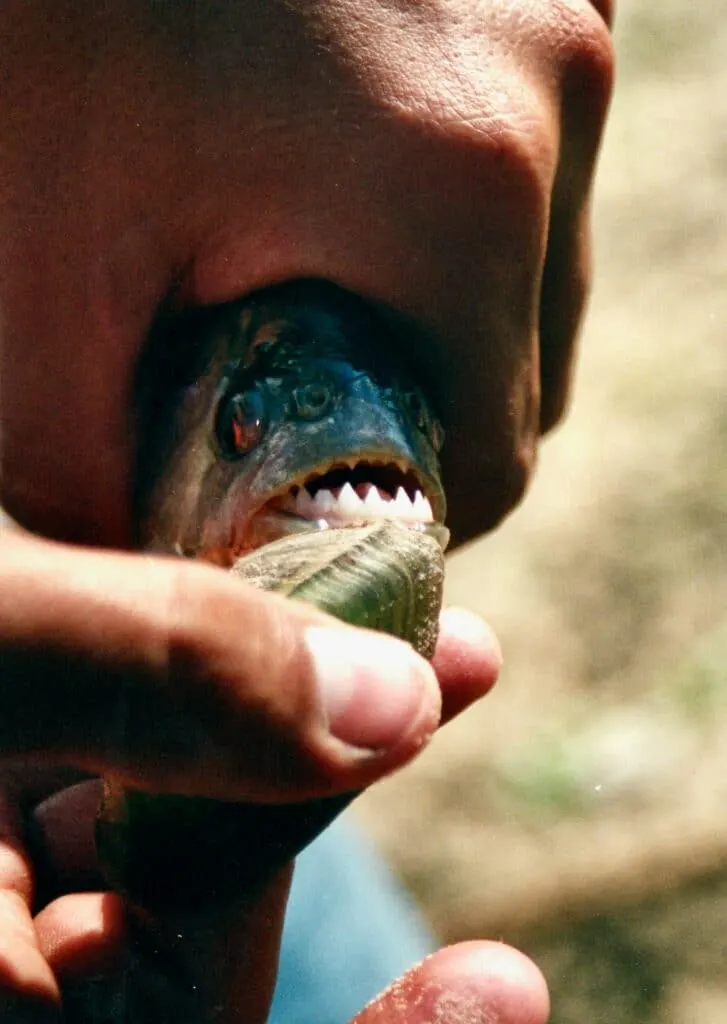
The Piranha is a predator many people fear in the captivating realm of freshwater habitats, where various fascinating organisms abound. It is one of the South American rivers’ most infamous denizens known for its razor-sharp teeth and vicious feeding frenzy. In this article, we dive into the fascinating world of the Piranha, learning about its distinct traits, habitat, behavior, and the dreadful adaptations that make it such a ferocious predator.

Skip ahead to any section below!
An Overview Of The Piranha

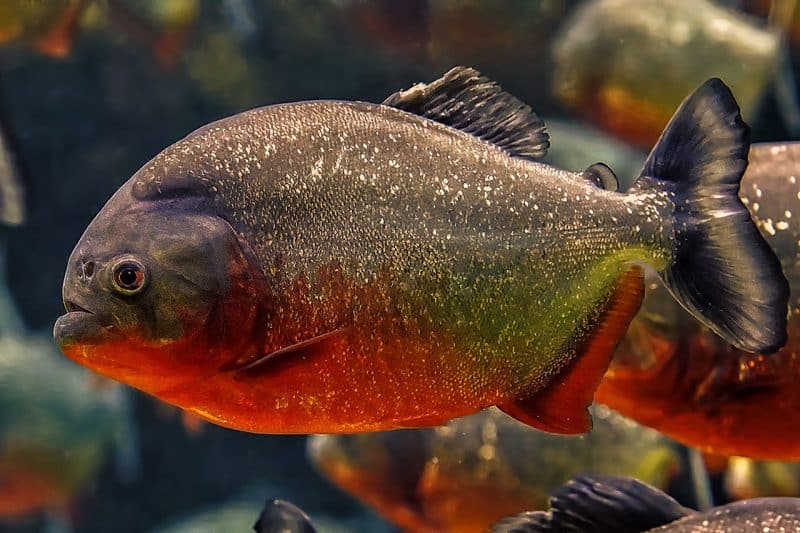
The Piranha is a predatory fish in South American rivers and lakes. It is a member of the Serrasalmidae family. There are several other kinds of piranhas, such as the notorious red piranha (Pygocentrus piraya), the black piranha (Serrasalmus rhombeus), and the red-bellied piranha (Pygocentrus nattereri). They have spawned many tales and stories about their ferocity because of their reputation for having sharp teeth and ravenous hunger.
Additionally, the Piranha is a member of the Characiformes order, which also comprises other fish species. It belongs to the freshwater fish family known as Serrasalmidae, mainly found in South America. These fish can hunt quickly and nimbly because of their sleek bodies, complemented by their sharp, interlocking teeth.
Check out: Largest Australian Shepherd.
Physical Characteristics Of The Piranha
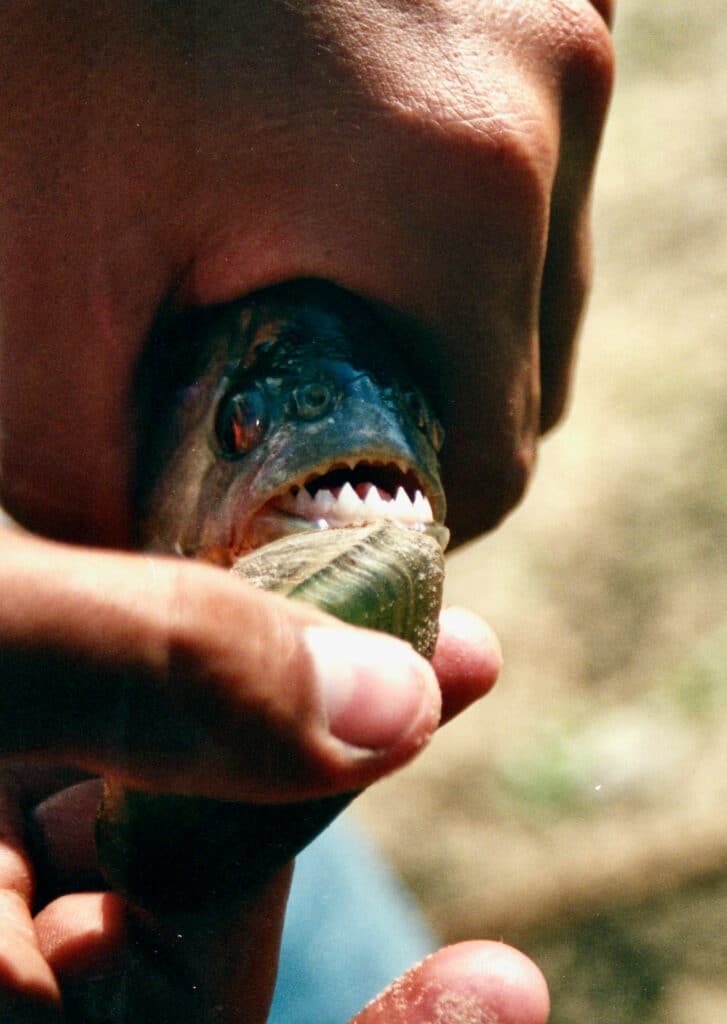
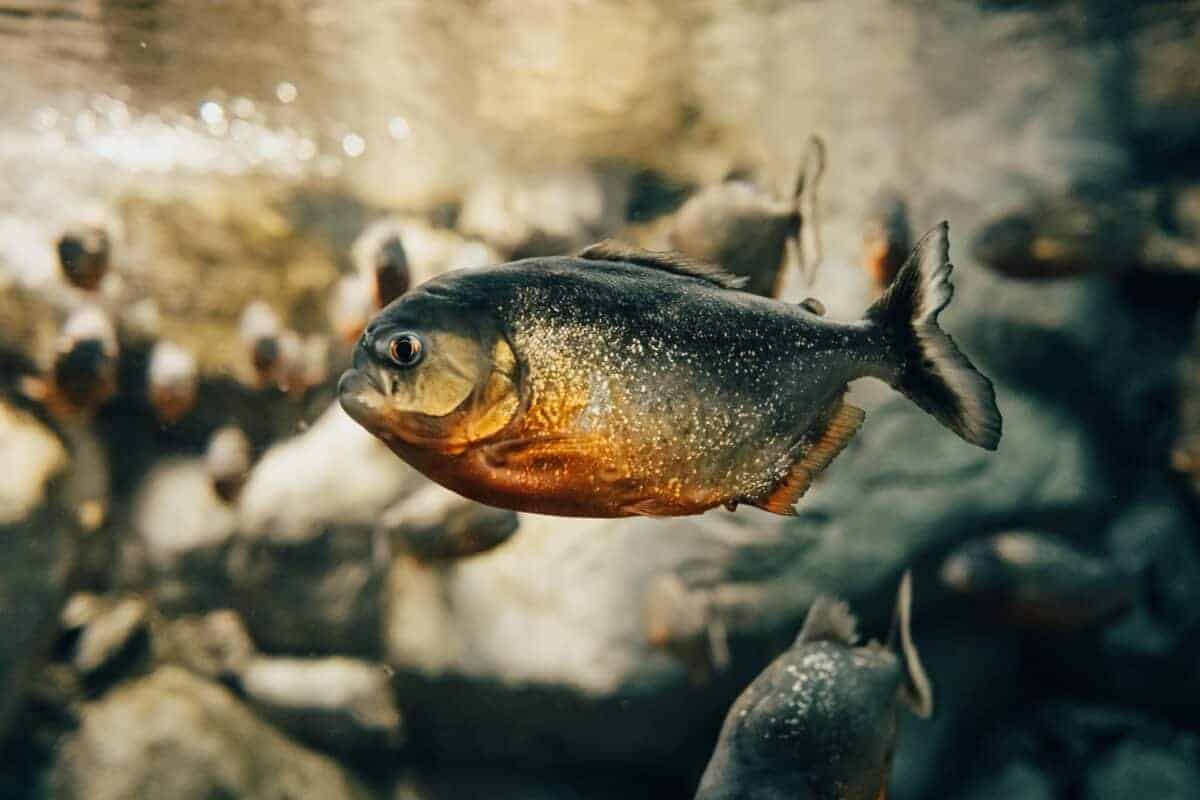
Piranhas come in different sizes depending on the species. The usual length of an adult piranha is between 15 to 50 centimeters or 6 to 20 inches. One of the most prevalent species, the red-bellied Piranha, often reaches 10 inches in length (25 centimeters).
- Body Type And Colour
Piranhas have a laterally compressed body type, facilitating fast swimming and aquatic movement. Different species of piranhas have different colorings, ranging from red-orange, silver, or olive-green bellies, like the red-bellied Piranha, and some may have stunning patterns.
- Jaw Structure and Teeth
Piranhas have triangular, sharp teeth interning when the mouth is closed. The teeth’s serrated edges make it possible to tear flesh with ease. They help to rip apart their prey and break through their bones.
Check out: Boomslang Snake Bite.
Habitat and Distribution Of The Piranha
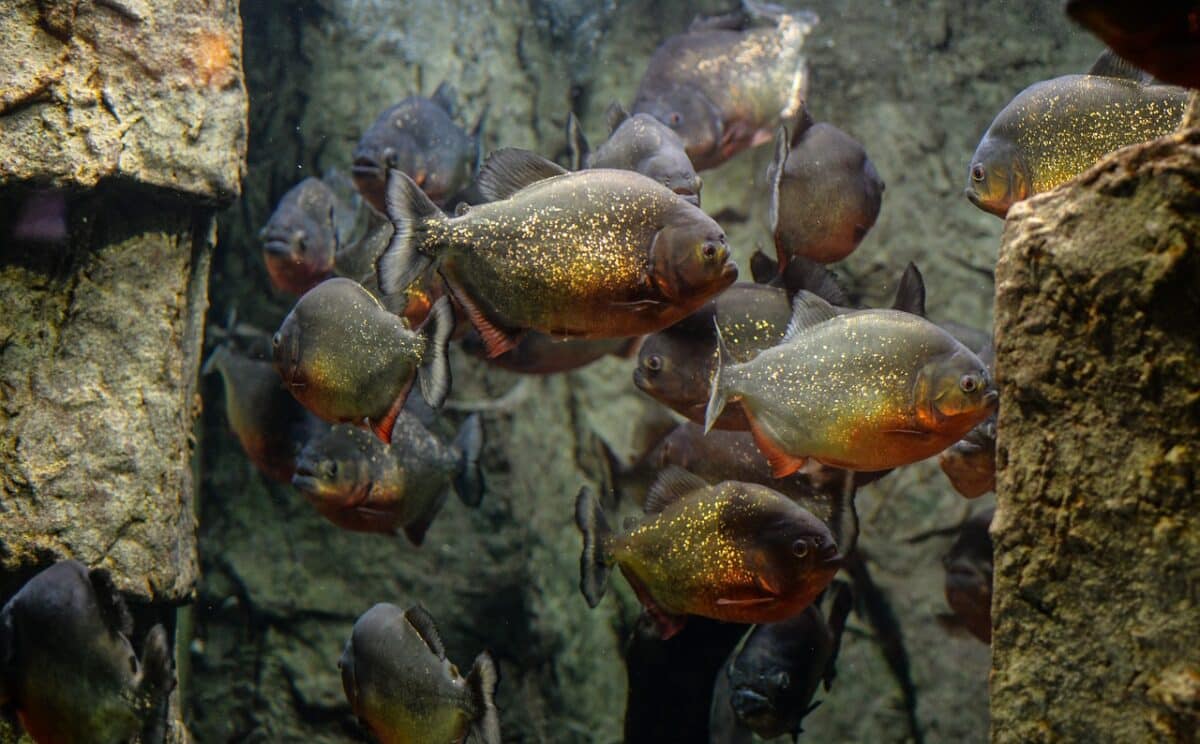

The Piranhas are usually found in the freshwater rivers, lakes, and swamped forests of South America. They usually reside in countries that make up the Amazon River basin, including Brazil, Peru, Colombia, and Venezuela. Besides, the Piranhas may live in harmony with a wide variety of aquatic species in their habitats’ warm, tropical settings.
Check out: Horned Viper Snake Bite.
Behavior and Feeding Patterns Of The Piranha
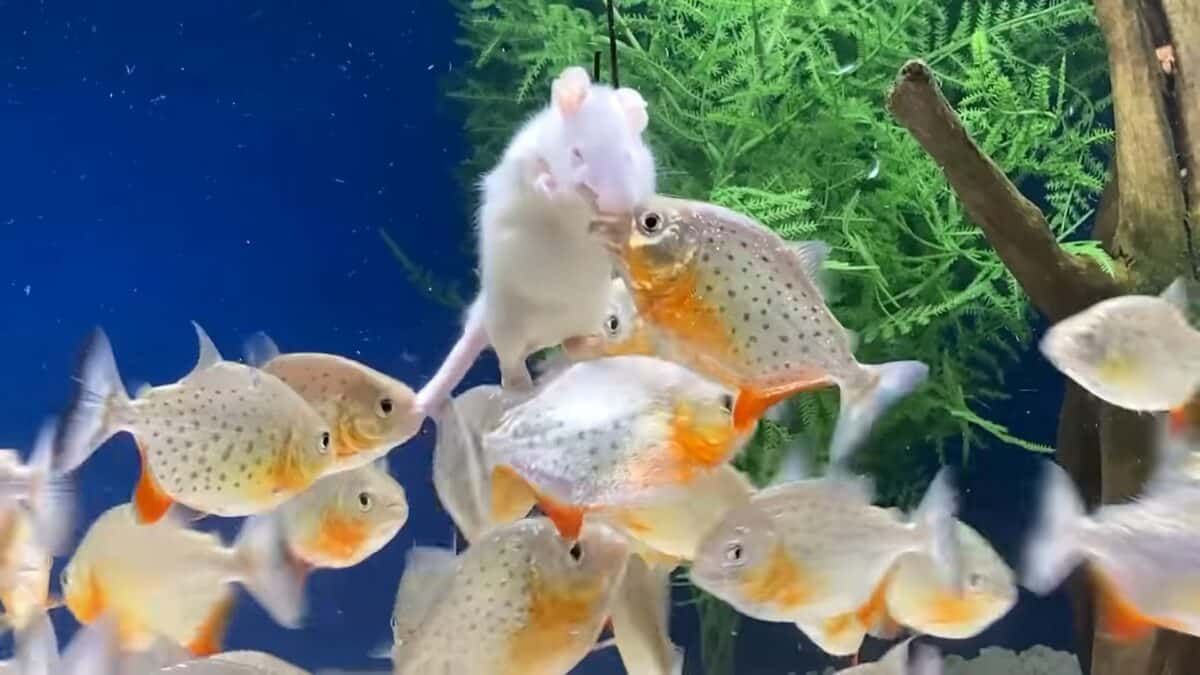

Piranhas are opportunistic carnivores known for their razor-sharp teeth and ravenous appetite. Although fish make up most of their diet, they occasionally feed on other aquatic species like insects, crabs, and even small animals. They eat their prey efficiently by tearing it apart with razor-sharp teeth.
Piranhas are sociable fish that frequently group in schools, mainly when foraging or under stress. The development of schools boosts hunting efficiency while offering safety from predators. Besides, schools of feeding piranhas are recognized for their synchronized feeding behavior. They overwhelm their prey by proceeding in schools. In fact, they are known for acting aggressively towards their own fellows, especially during the breeding season or when food is scarce.
Breeding and Reproduction Of Piranhas
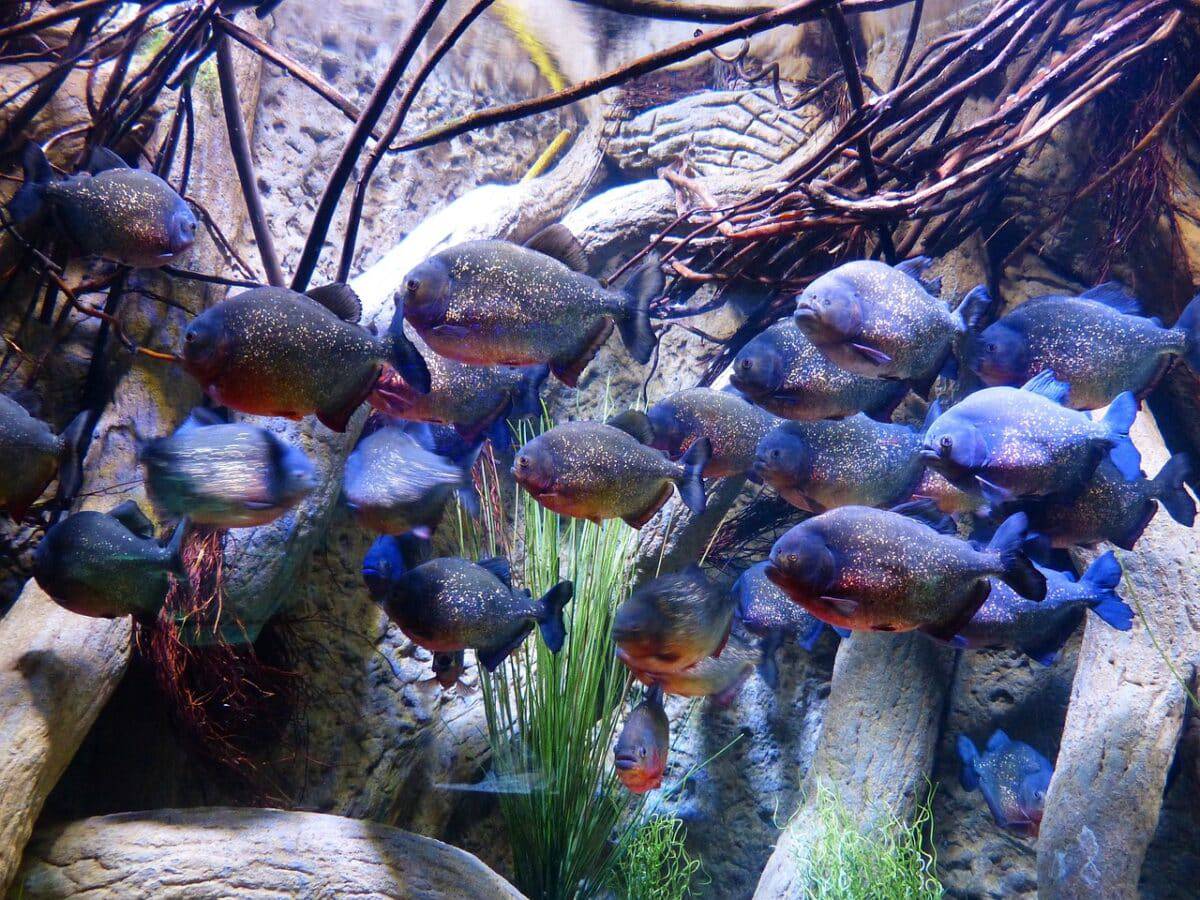

The rainy season when water levels are high is the ideal setting for spawning piranhas. Male piranhas frequently perform courtship behaviors, including fin displays, circling, and biting to entice females. After a pair has mated, the female constructs a nest, generally in submerged vegetation or other suitable objects, and lays her eggs there.
In some piranha species, both parents help to watch after and safeguard the eggs. They fiercely protect the nest from potential dangers to ensure the survival of their young. The juvenile piranhas are then raised by their parents when they hatch until they reach maturity and are able to survive and eat independently.
How Piranhas Adapt To The Predator-Prey Dynamics
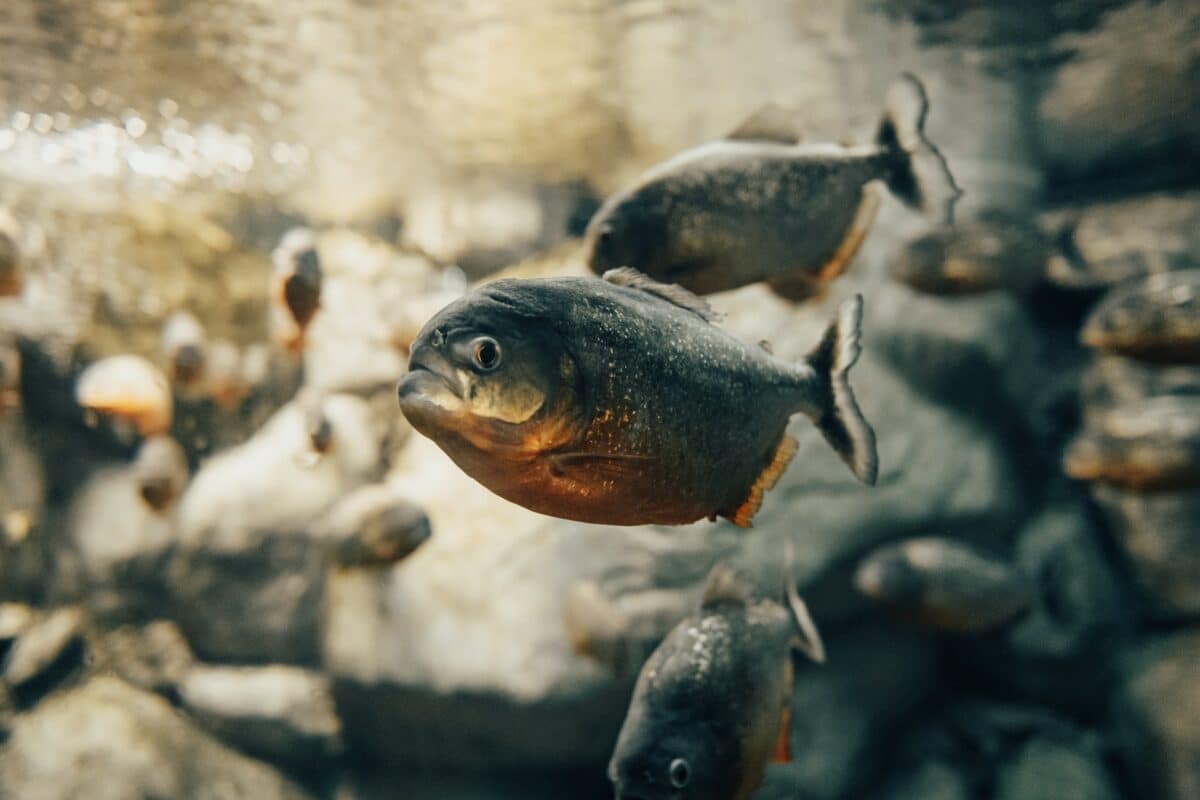

Although piranhas are fierce predators, they also have to worry about being eaten by larger fish, caimans, river dolphins, and birds of prey. Young piranhas are particularly susceptible to predation because of their tiny size and underdeveloped defensive capabilities.
However, Piranhas are blessed with good vision and acute sensory systems that aid in locating their prey or identifying potential predators. They also have a well-developed lateral line system that helps identify possible games by detecting movement and vibrations in the water.
The most noticeable adaptations for feeding in piranhas are their razor-sharp teeth and strong jaws. Using their teeth may cause severe injuries to their prey and soon render their victims helpless.
Relationship With Other Oceanic Animals
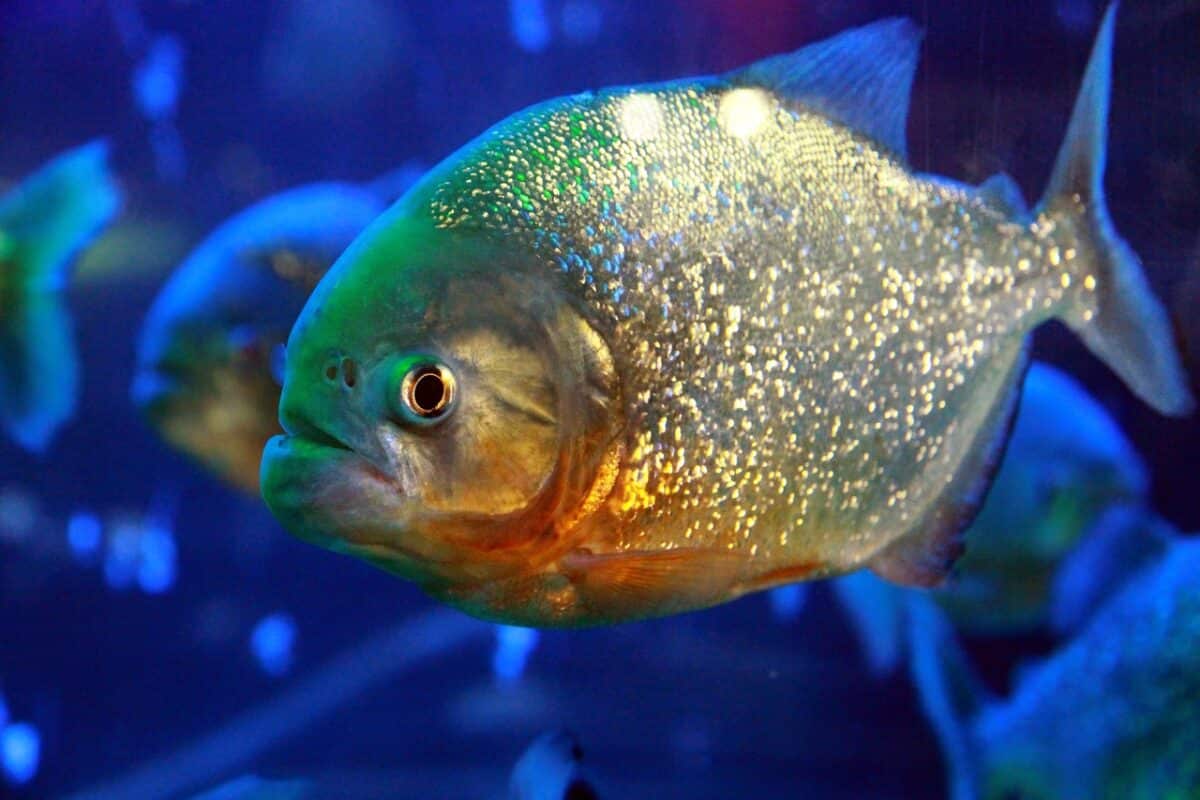

Piranhas enjoy interactions with other aquatic species and play a vital role in preserving the equilibrium of the ecosystem. They prevent overpopulation and maintain the general well-being of the marine community by acting as predators and reducing the number of smaller fish, insects, and crustaceans.
Additionally, piranhas contribute to the complex food web of their habitat by providing food for larger predatory fish and birds. Though frequently feared, piranhas serve an important ecological function by illuminating the interconnectedness and intricate interactions among species in aquatic ecosystems.
Ecological Importance
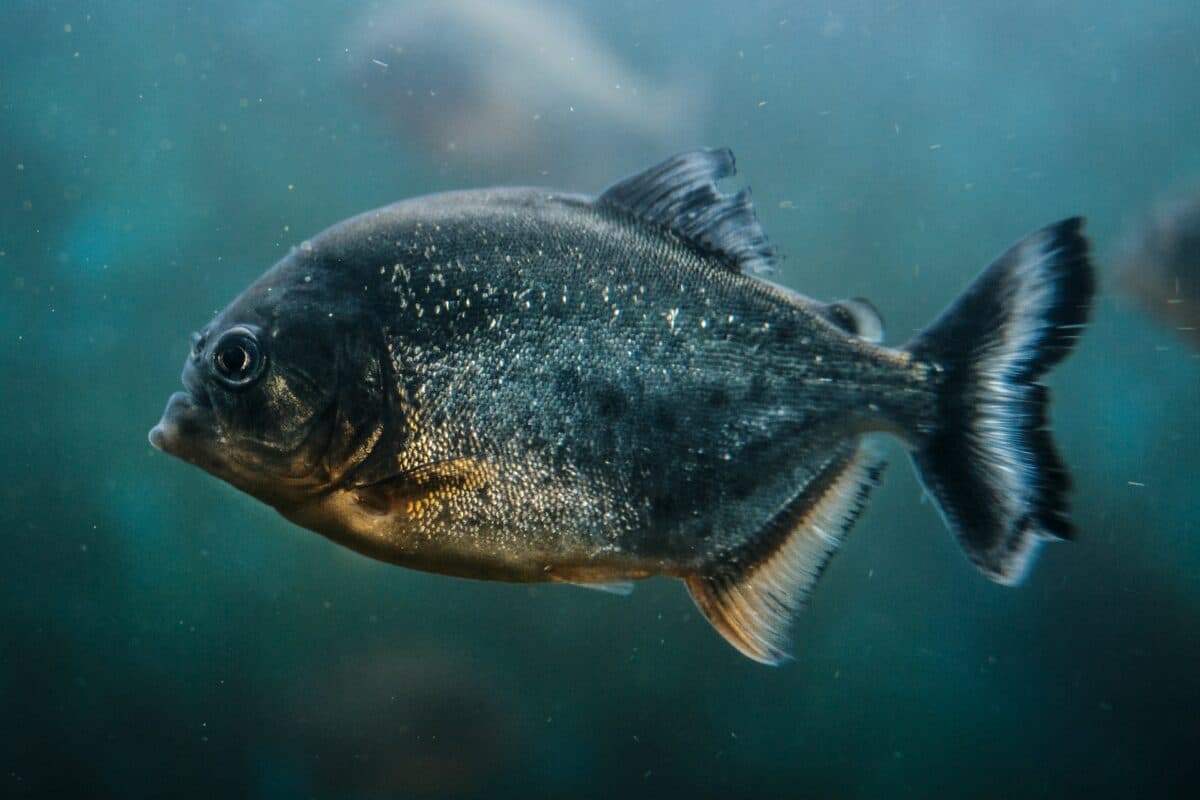

Despite its notorious image, piranhas play an essential ecological role in freshwater habitats. The Piranha, a top predator, contributes to the control of other fish species’ numbers in its ecosystem. The Piranha prevents smaller fish from becoming overabundant by eating them, maintaining the ecosystem’s balance and health.
The feeding habits of piranhas also help with the cycling of nutrients. When they eat their prey, they release nutrients into the ecosystem through their excrement, giving other creatures a crucial supply of nutrients. Moreover, piranhas contribute to the complex web of trophic interactions in the ecosystem by serving as a food source for larger predators like caimans and river dolphins.
Conservation Status
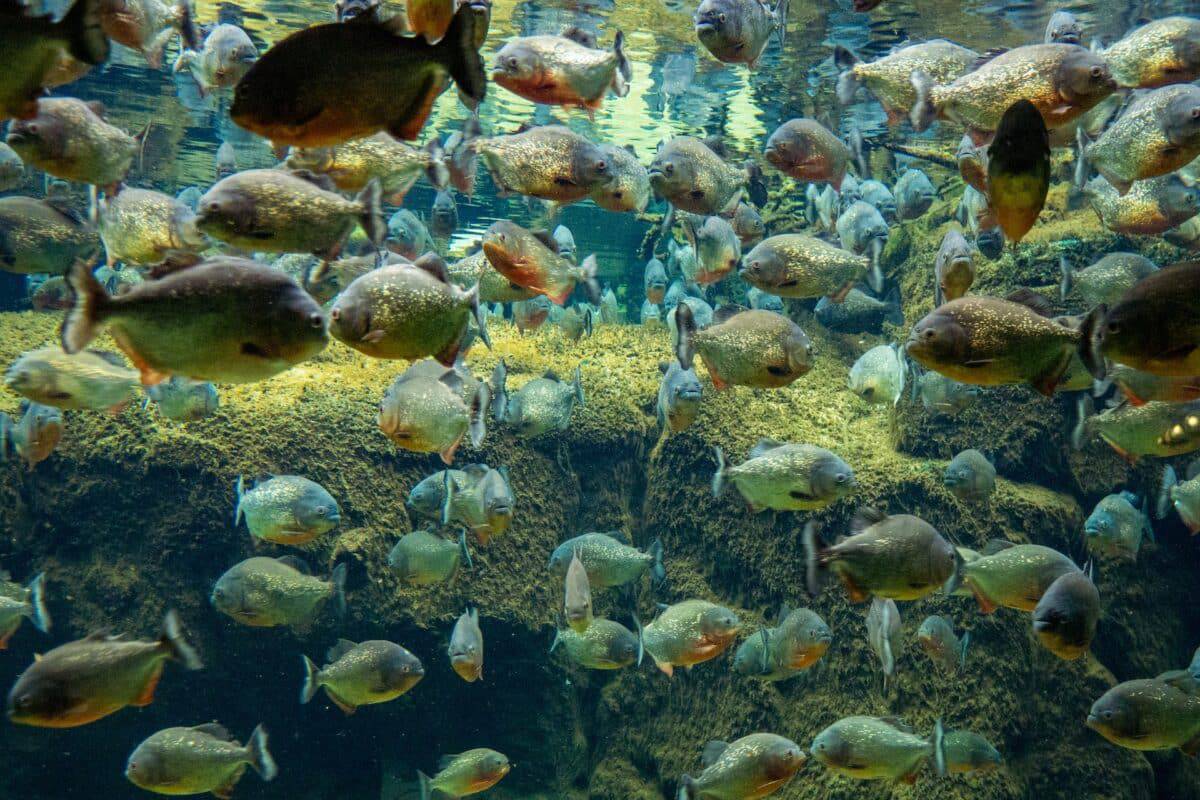

Depending on the species, different piranhas have different conservation statuses. Significant risks include pollution, overfishing, and habitat degradation. Their aquatic habitats and connectivity are disrupted by deforestation, and water quality is decreased by pollution. Addressing these dangers and implementing efficient conservation measures are necessary to protect piranhas and their freshwater environments.
Additionally, population decline and the potential introduction of non-native species are caused by overfishing for food and the aquarium trade. Protecting habitat, using sustainable land-use methods, practicing ethical fishing, and upholding laws should be the primary goals of conservation initiatives. Education and public awareness are essential for shifting unfavorable attitudes and recognising their ecological significance.
FAQs
- Are Piranhas Harmful To Humans?
Despite their reputation as being dangerous, piranhas rarely harm humans. They tend to be shy and avoid interacting with humans. However, one must be cautious when interacting with them in the wild because they might turn hostile if they feel threatened or are in a feeding frenzy.
- What Do Piranhas Consume?
Piranhas feed on fish, insects, crustaceans, small mammals, and birds that stray too close to the water. As opportunistic feeders, they will eat damaged prey or scavenge on carcasses.
- Do Piranhas Make Good Pets?
Piranhas can be maintained as pets, but only under certain circumstances. They require sizable tanks with lots of room for swimming and hiding spots. Their diet must include suitable food sources and the water should be properly kept and purified.
Key Points
| 1. The Piranha is a feared freshwater predator known for its sharp teeth and vicious feeding frenzy. |
| 2. Piranhas have distinct physical characteristics, including different sizes, body types, colors, and jaw structures. |
| 3. They inhabit freshwater habitats in South America, particularly in the Amazon River basin. |
| 4. Piranhas are opportunistic carnivores, feeding on fish, insects, crustaceans, and small animals. |
| 5. Piranhas play an important ecological role by controlling fish populations and contributing to nutrient cycling. |
Bottom Line
Only a few predators are as revered and fascinating in freshwater habitats as the Piranha. Piranhas have earned a legendary status as a representation of the Amazon and other South American rivers, thanks to their powerful teeth, symbiotic hunting methods, and adaptability to various settings.
There is no denying their reputation as expert and effective hunters, even though their reputation as man-eating monsters is mostly overblown. The Piranha serves as a reminder of the remarkable diversity and fantastic nature of our planet’s fauna as we continue to research and comprehend the complex dynamics of these ecosystems.
If you’re looking for more articles like this, look no further! Check out our related animal articles below.
Next up: Wildlife Spotlights: Gorilla And Anaconda In Focus, Watch Two Kids Swim Near Great White Shark, Explore Florida’s Bull Shark Population, Okapi: The Elusive Forest Giraffe, and Michael Phelps Vs. Dolphin: A Race For Aquatic Supremacy.
- Watch: Lizard Greets Man like a Dog! - April 25, 2024
- Mama Deer Is So Worried About Her Baby - April 25, 2024
- Watch Innocent Baby Bird Walks up to Leopard – Wild Ending! - April 25, 2024


