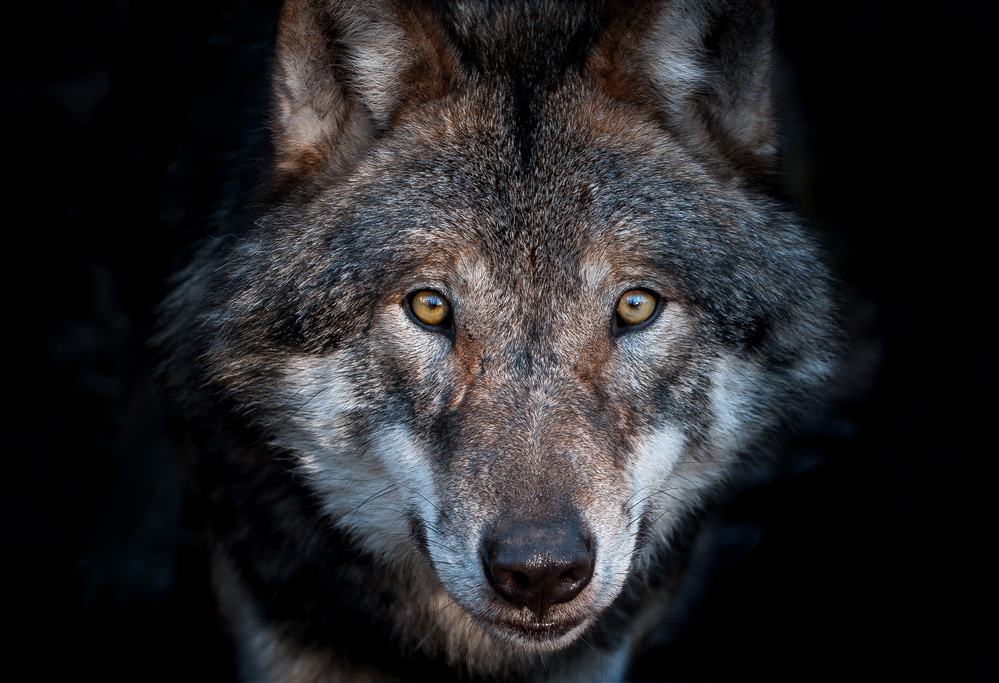
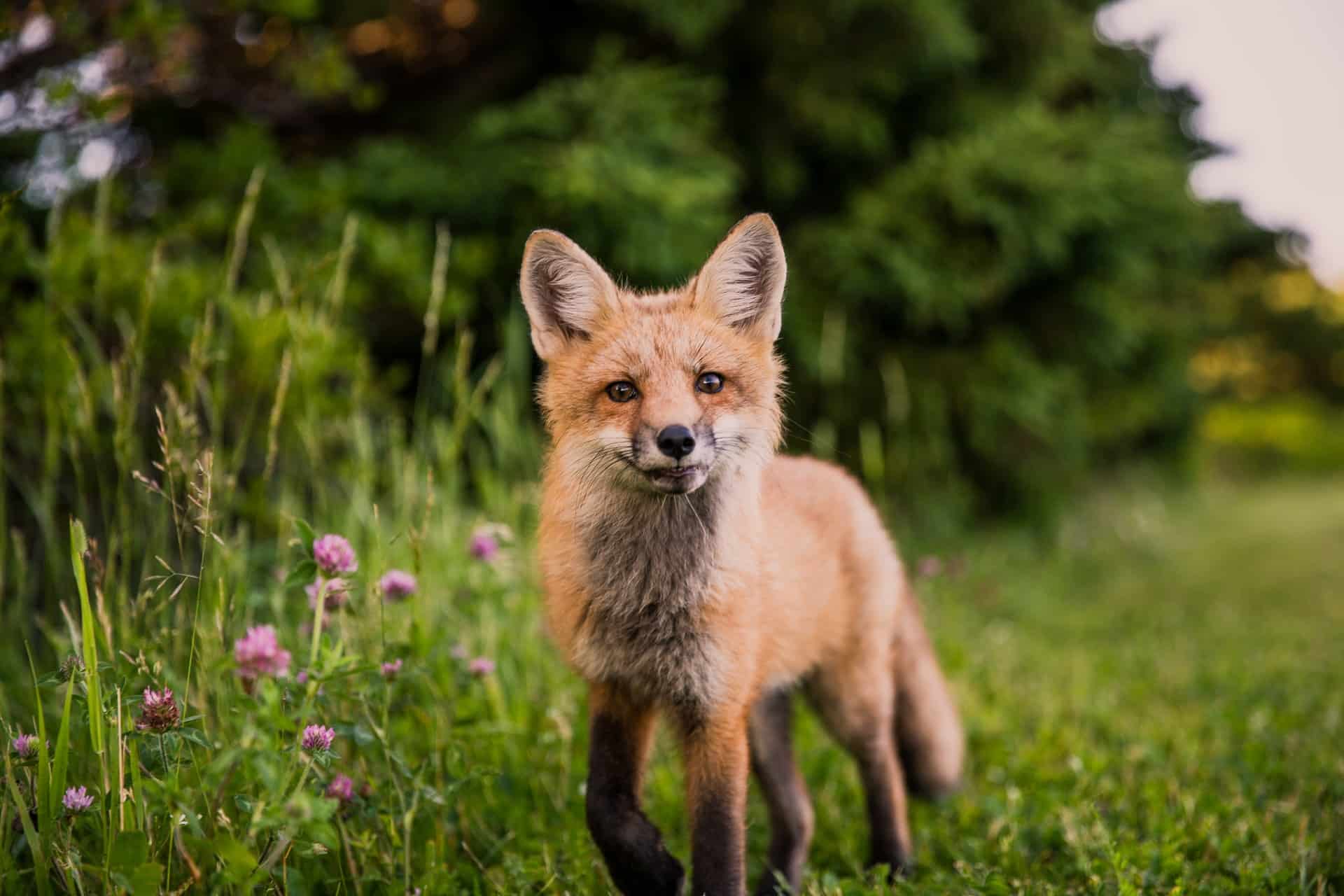
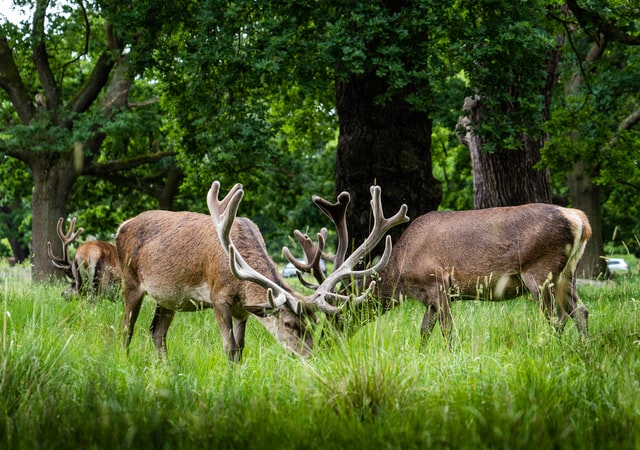
Europe, a continent rich in diversity, offers a fascinating variety of animals and wildlife. From the Iberian lynx in Spain to the majestic brown bear in Romania, Europe’s wildlife is as varied as its landscapes. Importantly, conservation efforts across the continent are crucial in protecting these species.
Dive Into The Animals and Wildlife in Europe and Where to Find Them
- Explore The Azores

- Animals and Wildlife in Germany

- Wildlife of Sweden
- Animals in Greece

- Enchanting Wildlife of Europe: A Symphony of Beauty

- Sicily’s Sea Urchin Debacle: A Delicacy at the Brink of Extinction

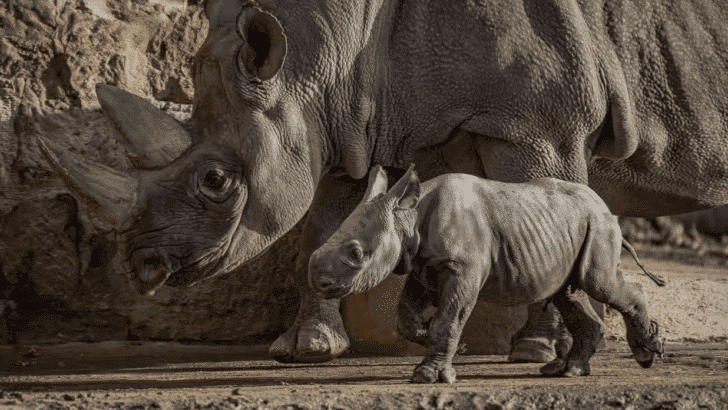
- Critically Endangered: Watch Black Rhino Born at Chester Zoo

- Growing and Caring for the Leyland Cypress

- Animals and Wildlife in France

- Animals and Wildlife in Italy

- Animals and Wildlife in Spain

- Animals and Wildlife in England

- Top 10 Animal Encounters in Europe

Rewilding efforts are made across Europe by “Rewilding Europe“. Feel free to support them as they took on the crucial task of giving wildlife some of their natural land back.
Iconic Animals of 20 European Countries: A Snapshot of the Diversity of Animals and Wildlife in Europe
This following table offers a glimpse into some of these remarkable creatures, underscoring the importance of conservation efforts across Europe to protect these natural treasures for future generations.
| Country | Iconic Animal |
|---|---|
| Spain | Iberian Lynx |
| Norway | Moose |
| United Kingdom | Red Fox |
| France | European Brown Bear |
| Italy | Marsican Brown Bear |
| Greece | Loggerhead Sea Turtle |
| Germany | European Bison |
| Sweden | Eurasian Lynx |
| Finland | Brown Bear |
| Poland | White Stork |
| Switzerland | Alpine Ibex |
| Portugal | Iberian Wolf |
| Russia | Siberian Tiger |
| Romania | Carpathian Lynx |
| Iceland | Arctic Fox |
| Ireland | Irish Hare |
| Netherlands | Red Deer |
| Belgium | European Badger |
| Austria | Golden Eagle |
| Denmark | European Hedgehog |
If you have any feedback please reach out to us via feedback@animalsaroundtheglobe.com.
Read more about all kinds of animal lists, locations, and Expert insights here.
Newest Category: Animals and Wildlife in Europe
- 5 Best Places to See African Wild Dogs - April 24, 2024
- Best Places to See Giant Pandas - April 23, 2024
- Sea Snakes: A Complete Guide - April 23, 2024